Table of Contents
- MP Full Form: Introduction
- MP Full Form: Powers
- MP Full Form: Functions
- MP Full Form: Challenges
- MP Full Form: Election & Representation
- MP Full Form: Roles & Responsibilities
- MP Full Form: Parliament Sessions & Committees
- MP Full Form: Engagement with Constituents
- MP Full Form: Conclusion
- MP Full Form: FAQs
MP Full Form: Introduction

MPs are responsible for making laws that govern the country. They do this by debating and voting on bills that are introduced by the government or by private members.
MPs are responsible for holding the government to account for its actions. They do this by asking questions in Parliament, by scrutinizing government policy, and by voting on government bills.
MP Full Form: Powers
Legislative Power: MPs have the authority to draft, propose, debate, amend, and vote on legal guidelines that govern the nation.
Budget Approval: MPs review, debate, and approve the country wide budget, influencing the allocation of funds to diverse sectors.
Government Oversight: MPs monitor and query the movements of the authorities, ensuring transparency and duty.
Representation: MPs represent the hobbies and needs in their constituents, voicing their worries in parliament.
Policy Influence: Through debates and committee paintings, MPs shape and influence public coverage and national priorities.
Approval of Treaties and Appointments: In many parliaments, MPs have the electricity to approve treaties, agreements, and key government appointments.
Constituency Services: MPs can address neighborhood troubles, endorse for assets, and useful resource residents with governmental concerns, ensuring their parts’ desires are met.
MP Full Form: Functions
Lawmaking and Policy Formulation: MPs make a contribution to the system of public policies via the drafting and passing of laws that mirror the u . S . A .’s wishes and priorities.
Constituency Advocacy: MPs act as advocates for his or her ingredients, making sure local troubles are addressed through the government and facilitating access to public offerings.
Holding the Executive Accountable: MPs question the movements of the government department, ensure the government is appearing in the public hobby, and undertaking policies thru debates and inquiries.
Scrutinizing Legislation: MPs cautiously assessment and examine payments, suggesting amendments to make sure the rules is powerful, truthful, and aligned with countrywide goals.
Promoting Public Awareness: MPs increase attention of country wide or global problems, the usage of their platform to inform the general public and inspire informed political participation.
Intervening in National Crises: MPs play an vital position in discussing and formulating responses to national crises, including financial downturns, public health emergencies, or security threats.
Engagement in International Affairs: MPs may also have an effect on overseas coverage decisions, global agreements, and diplomatic members of the family via debates, committees, or in collaboration with different countries’ representatives.
MP Full Form: Challenges
Balancing Constituency and National Interests: MPs regularly struggle to deal with the neighborhood needs in their materials while making decisions that advantage the state as an entire, that can sometimes be in war.
Political Polarization: Increasing political divisions can avert productive debates and cooperation, making it difficult for MPs to work throughout birthday celebration traces to skip law or discover common floor.
Pressure from Political Parties: MPs may additionally face stress from their political parties to vote or act in positive methods, which could limit their independence and private judgment.
Limited Resources and Time: MPs have numerous duties, including attending periods, serving on committees, and helping materials, all of that may strain their time and available sources.
Public Scrutiny and Accountability: MPs are often below severe scrutiny from the media and the public, and any misstep or failure can result in a lack of credibility or political support.
Corruption and Ethics Concerns: MPs may be prone to corrupt practices, conflicts of hobby, or undue influence from powerful companies, which could harm public consider in the legislative system.
Ineffectiveness in Addressing Complex Issues: Due to the complexity of current-day problems (like climate alternate, global fitness, or technological development), MPs may battle to create powerful, long-term solutions that address those demanding situations.
MP Full Form: Election & Representation
- The Democratic Mandate
MPs are elected through a democratic voting process, where citizens exercise their right to choose representatives who will voice their concerns and interests at the national level.
- Constituency Connection
MPs represent specific geographical constituencies, forging a vital link between the citizens’ aspirations and the legislative decisions that impact their lives.

MP Full Form: Roles & Responsibilities
- Lawmaking: Crafting Legislation
MPs actively participate in parliamentary debates, proposing, amending, and passing laws that reflect the needs and values of their constituents. - Oversight and Accountability
MPs hold the government accountable by scrutinizing its actions, policies, and expenditures, ensuring transparency, and safeguarding the interests of the public. - Representing Constituents’ Interests
MPs act as the voice of their constituents, conveying their concerns, advocating for policies, and seeking solutions to local and national issues.
MP Full Form: Parliament Sessions & Committees
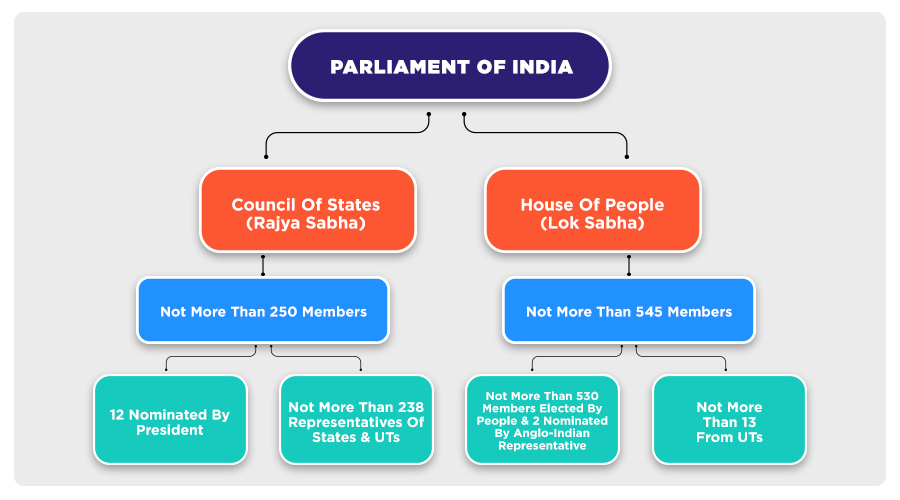
- Participating in Debates and Discussions
MPs contribute to parliamentary sessions, engaging in debates on matters of national importance, and expressing their perspectives on various issues.
- Committee Work: Specialized Focus
MPs serve on committees dedicated to specific areas such as finance, health, and education, where they delve deeper into policy matters and provide expert insights.
MP Full Form: Engagement with Constituents
| Engagement Method | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constituency office | The MP has an office in their constituency where constituents can come to meet with them, speak to their staff, or leave messages. | Constituents can get to know their MP and feel like they have a direct line of communication with them. The MP can build relationships with constituents and learn about their concerns. | The MP’s office may be busy and it can be difficult to get an appointment. Constituents may not be able to travel to the office if it is not located in their community. |
| Town hall meetings | The MP holds regular meetings in their constituency where constituents can come and ask questions, share their concerns, and hear about the MP’s work. | Town hall meetings are a good way for the MP to connect with a large number of constituents at once. They can also be a way for the MP to get feedback on their work and to address concerns that are shared by many people. | Town hall meetings can be disruptive and difficult to organize. The MP may not be able to answer all of the questions that are asked. |
| Social media | The MP can use social media to connect with constituents, share information about their work, and answer questions. | Social media is a cost-effective way to reach a large number of people. It can also be a way for the MP to connect with constituents who are not able to attend in-person meetings. | Social media can be a noisy environment and it can be difficult to get people’s attention. The MP’s messages may be lost in the shuffle. |
| Letters and emails | The MP can invite constituents to write to them or email them with questions or concerns. | Letters and emails are a good way for constituents to communicate with the MP without having to travel to their office or attend a town hall meeting. | The MP may receive a large volume of letters and emails, which can make it difficult to respond to everyone. |
| Surveys | The MP can conduct surveys of constituents to get their feedback on a variety of issues. | Surveys are a good way to get a sense of what is important to constituents and to identify areas where the MP can improve their work. | Surveys can be expensive to conduct and it can be difficult to get a representative sample of the population. |
| One-on-one meetings | The MP can meet with constituents one-on-one to discuss their concerns. | One-on-one meetings are a good way for the MP to get to know constituents and to understand their specific needs. | One-on-one meetings can be time-consuming and it can be difficult to meet with everyone who requests a meeting. |
MP Full Form: Conclusion
FAQs
Q1: What is the role of an MP?
A: MP represents their constituents in the legislature, participates in making laws, debates national issues, and holds the government accountable.
Q2: How are MPs elected?
A: MPs are elected through general elections, typically in single-member constituencies, where voters choose their preferred candidate. The candidate with the most votes wins.
Q3: What are the main duties of an MP?
A: MPs debate laws, represent their constituents, monitor government actions, serve on parliamentary committees, and vote on legislation.
Q4: How long do MPs serve in office?
A: The term length for MPs varies by country. For example, in India, MPs serve a five-year term unless a general election is called earlier.
Q5: Can MPs change political parties?
A: Yes, MPs can change political parties, although it may impact their reputation and relationships with their constituents or party members.



















