Ultraviolet (UV) light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has shorter wavelengths than visible light, but longer than X-rays. It is invisible to the human eye, but some insects, such as bumblebees, can see it.
UV light is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is divided into three main types: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
Introduction
Have you ever basked in the warmth of sunlight on a clear day? That soothing feeling comes from more than just light; it’s the embrace of the sun’s rays, including a spectrum we often overlook—ultraviolet (UV) light.
Welcome to the UV Spectrum: A Brief Overview
Imagine sunlight as a beautiful blend of colors, like the rainbow after a rainstorm. The colors we see—reds, oranges, blues—are just part of a vast spectrum of light, ranging from long, gentle waves to short, energetic ones. Among them, unseen by our eyes, lies UV light.
Ultraviolet light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, situated between the visible light we perceive and X-rays. Though invisible to us, UV light plays a significant role in our lives, affecting our health, environment, and technology.
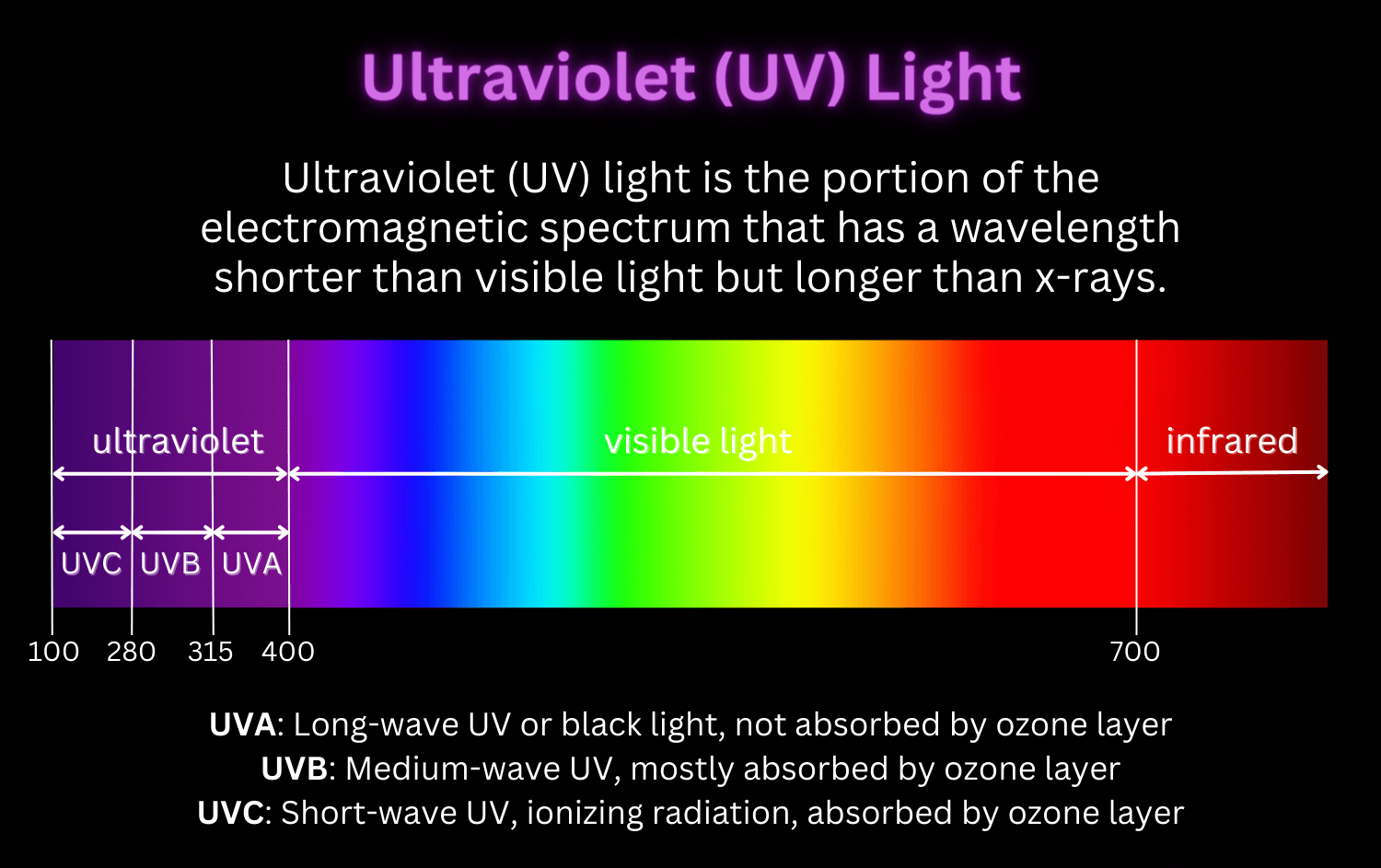
types of UV light
When we talk about ultraviolet (UV) light, we’re actually referring to a spectrum that comprises different types of UV rays. These rays are categorized based on their wavelengths and how they interact with matter. Let’s take a closer look at the three main types of UV light: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
1. UVA (Longwave Ultraviolet Light)
UVA rays have the longest wavelengths among UV light types. They are the most prevalent and least energetic of the UV rays that reach the Earth’s surface. Although less powerful, UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, making up about 95% of the UV radiation that reaches us. They play a role in premature skin aging and can contribute to skin cancer development.
2. UVB (Mediumwave Ultraviolet Light)
UVB rays have shorter wavelengths and are more energetic than UVA rays. They are responsible for sunburns and play a major role in skin cancer development. While the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs a portion of UVB rays, enough of them reach the surface to cause significant impact on our skin.
3. UVC (Shortwave Ultraviolet Light)
UVC rays have the shortest wavelengths and the highest energy levels of all UV rays. Fortunately, the Earth’s atmosphere filters out UVC rays, so they don’t naturally reach us from the sun. However, UVC light is used for germicidal purposes, such as disinfecting air, water, and surfaces, due to its ability to destroy or inactivate microorganisms.
Sources of Ultraviolet (UV) Light
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Sunlight | The sun is the primary source of UV light. Its powerful fusion reactions emit a broad spectrum of radiation, including UV rays. When sunlight reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, it contains three types of UV rays: UVA, UVB, and UVC. However, due to the Earth’s protective ozone layer, most UVC and a portion of UVB are absorbed, allowing essential UVA and a fraction of UVB to reach us. |
| Celestial Sources | Beyond our sun, celestial bodies like stars, galaxies, and other cosmic phenomena emit UV light. Telescopes and space-based observatories enable scientists to study this extraterrestrial UV radiation, providing valuable insights into the universe’s composition and behavior. |
| Artificial Sources | In addition to natural sources, humans have created artificial sources of UV light for various purposes, including medical, industrial, and commercial applications. These sources include: |
| – UV Lamps and Bulbs | UV lamps and bulbs are designed to emit UV light when powered. They come in various types, such as mercury vapor lamps and low-pressure mercury lamps. These are utilized in industries, laboratories, and healthcare for applications like sterilization, curing coatings, and scientific research. |
| – UV LEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes) | UV LEDs are energy-efficient light sources that emit UV light when an electric current is passed through them. They find applications in disinfection, water purification, counterfeit detection, and even insect traps. |
UV Light and Human Health
Ultraviolet (UV) light, while vital for life and health in moderation, can also pose risks if exposure is excessive. Let’s navigate through the delicate balance between UV light and human well-being.
1. Positive Effects of UV Light
UV light plays a crucial role in our health, primarily through its interaction with our skin and the production of vitamin D. Here’s how:
a. Vitamin D Synthesis
When our skin is exposed to UVB rays from the sun, it triggers the production of vitamin D, a nutrient essential for bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
b. Mood Enhancement
Sunlight, including UV rays, can boost mood by stimulating the production of serotonin—a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of happiness and well-being.
2. Negative Effects of UV Light
While some UV exposure is beneficial, overexposure can have adverse effects on our health, primarily on our skin and eyes:
a. Skin Damage and Cancer
Excessive UV exposure can cause sunburn, and premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer. Both UVA and UVB rays can contribute to these effects.
b. Eye Damage
Prolonged exposure to UV light can harm the eyes, leading to conditions such as cataracts, pterygium, and macular degeneration.
3. Balancing UV Exposure for Health
Achieving a balance in UV exposure is key to reaping the benefits while minimizing risks:
a. Moderation and Protection
Limit sun exposure during peak UV hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
Use sunscreen with a high SPF and wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
b. Regular Screenings
Schedule regular skin checks with a dermatologist to detect any potential skin issues early.
Applications of Ultraviolet (UV) Light
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical and Healthcare | Utilized for disinfection and phototherapy to treat skin conditions. |
| – Sterilization and Disinfection | Used to disinfect air, water, and surfaces, killing harmful microorganisms. |
| – Phototherapy | Treatment for skin conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo using controlled UVB exposure. |
| Industrial and Commercial | Employed in curing processes, non-destructive testing, and other industrial applications. |
| – Curing and Printing | Used to cure inks, coatings, and adhesives, enhancing efficiency and product quality. |
| – Non-Destructive Testing | Detects flaws in materials to ensure the safety and reliability of components. |
| Consumer Products and Everyday Uses | Integrated into various consumer products for enhanced safety, efficiency, and convenience. |
| – Germicidal Lamps | Incorporated in water and air purifiers to kill bacteria, viruses, and microorganisms. |
| – Insect Traps | Attracts and traps insects for effective pest control both indoors and outdoors. |
| – UV Light in Art and Entertainment | Creatively used in glow-in-the-dark products, fluorescent paints, and artistic lighting. |
UV Light in Disinfection and Sterilization
Ultraviolet (UV) light, a natural component of sunlight, is a superhero in the battle against harmful pathogens. Its ability to disinfect and sterilize various surfaces and environments makes it a go-to tool for ensuring safety and cleanliness. Let’s shed light on how UV light works its magic to create healthier spaces.
1. How UV Light Works in Disinfection
UV light operates by disrupting the genetic material of microorganisms—bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens—preventing their ability to reproduce and ultimately rendering them harmless. It’s like a molecular kryptonite for these microscopic invaders.
2. Applications in Disinfection and Sterilization
a. Air Purification
UV light is employed to clean the air we breathe by neutralizing airborne pathogens, making it a vital tool in hospitals, schools, and crowded public places.
b. Water Treatment
In the realm of water purification, UV light is used to effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants present in water, ensuring safe drinking water for communities.
c. Surface Decontamination
UV light is utilized to disinfect surfaces in healthcare facilities, laboratories, and public spaces, reducing the risk of infections and promoting a sterile environment.
3. Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Compared to chemical disinfectants, UV light offers a non-toxic, eco-friendly approach to disinfection. It doesn’t leave behind any residues or harmful byproducts, making it a sustainable choice for maintaining hygiene.
4. Safety Measures
While UV light is an effective disinfection tool, precautions must be taken to avoid direct exposure to skin and eyes, as it can cause irritation. Proper training and safety protocols are essential to utilize UV light in a safe and efficient manner.
UV Light Safety Precautions
| Safety Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Wear Protective Gear | Use UV-blocking goggles or glasses and cover the skin to prevent direct UV exposure and irritation. |
| Avoid Direct Exposure | Never look at UV light sources without adequate protection as direct exposure can harm eyes and skin. |
| Use UV Light in Controlled Environments | Employ UV light in controlled, confined spaces, following safety guidelines for specific use. |
| Secure Proper Ventilation | Ensure adequate ventilation indoors to prevent harmful ozone accumulation from certain UV sources. |
| Follow Manufacturer Instructions | Adhere to manufacturer guidelines for safe operation, including recommended distances and durations. |
| Educate and Train | Provide education and training on UV light risks and safety procedures to minimize accidents. |
| Regular Maintenance and Checks | Perform routine maintenance to ensure UV equipment functions safely, promptly replacing faulty parts. |
| Emergency Preparedness | Be prepared for emergencies with eyewash stations, first-aid kits, and clear action plans for exposure. |
| Comply with Regulations | Follow local regulations and guidelines related to UV light usage to ensure legal compliance and safety. |
Conclusion
As we journeyed through the spectrum of ultraviolet (UV) light, we discovered a captivating realm of invisible energy that impacts our lives in multifaceted ways. UV light, though unseen to the naked eye, is a force to be reckoned with—a tool for good and a potential risk if not handled responsibly.
Navigating the Risks
However, like any powerful tool, UV light needs to be used with caution. Overexposure can lead to skin damage, premature aging, and even cancer. It’s crucial to strike a balance, embracing the sun for its benefits while taking precautions to shield ourselves from its potential harm.
A Brighter, Safer Future
As we conclude this journey through the UV spectrum, let’s carry forward the knowledge of UV light’s potential—both positive and negative. By respecting its power and using it wisely, we can harness the brilliance of UV light for a cleaner, healthier, and safer world. Let’s bask in the enlightening glow of understanding and ensure a brighter future for generations to come.
FAQs
UV light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that falls outside the range of visible light. It has shorter wavelengths and higher energy than visible light, making it invisible to the human eye.
UV light is classified into three main types based on wavelength:
- UVA (Longwave UV): Longer wavelengths, least energetic.
- UVB (Mediumwave UV): Intermediate wavelengths, moderately energetic.
- UVC (Shortwave UV): Shortest wavelengths, most energetic.
UV light primarily comes from the sun. It’s also emitted by artificial sources like UV lamps, bulbs, and UV LEDs used in various applications, including sterilization and disinfection.
UV light has both positive and negative effects on health. It helps in vitamin D production but can also cause skin aging and increase the risk of skin cancer with overexposure.
Read Also
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















