A wireless application protocol (WAP) is a set of protocols used when connecting to the Internet via wireless telecommunications devices. The WAP protocol utilises the markup language WML called Wireless Markup Language. The term “WAP” is sometimes used to describe both the overall technology and the protocols that make up the technology. WAP is the protocol for the wireless broadband Internet access service delivered by some mobile phone networks.
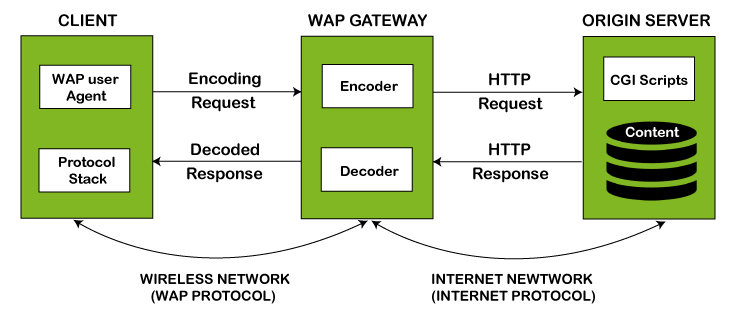
How WAP Works
WAP enables mobile devices to access the internet:
- Device and WAP Stack: Your mobile device communicates with a WAP stack, specialized for wireless communication.
- Request for Web Content: When you use your mobile browser, it sends a request to your carrier’s network.
- WAP Gateway: The request goes to a WAP gateway, which converts web content into a mobile-friendly format and manages security.
- Access to Web Servers: The gateway forwards the request to web servers.
- Content Conversion: Web server content is converted into formats like WML for mobile screens.
- Delivery to Your Device: The converted content is sent back to your mobile device.
- Interaction: You can interact with mobile-optimized web content.
WAP vs. Traditional Web Browsing
- Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) and traditional web development represent two distinct approaches to accessing online content, tailored to different contexts and devices.
- WAP is custom-made for mobile devices with small screens and limited processing power. It simplifies content with Wireless Markup Language (WML) and prioritizes essential information for efficient mobile use.
- WAP loads swiftly conserves data, and thrives in regions with shaky internet infrastructure. Security is enhanced through Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS). On the other hand, traditional web browsing caters to desktops and laptops with ample screen real estate and computational capabilities.
- It employs HTML for complex layouts, multimedia, and intricate interactions, offering a comprehensive web experience. While WAP is ideal for quick mobile tasks, like checking emails or basic searches, traditional web browsing shines in scenarios demanding a richer, multimedia-laden experience such as online shopping or multimedia content consumption.
WAP in Mobile Devices
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) has been a transformative technology within the realm of mobile devices. It emerged as a way to the task of turning in internet content to small-screened, aid-limited devices including early cell phones. WAP revolutionized mobile connectivity with the aid of allowing users to access net-primarily based statistics and offerings, correctly bringing the net to their wallet.
In its middle, WAP operates by means of translating preferred internet content into a format that fits cellular monitors and limited entry capabilities. This transformation is executed through using Wireless Markup Language (WML) and different mobile-unique languages. WAP additionally employs a stable communique layer, Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS), to guard records transmission over Wi-Fi networks.
One of the key benefits of WAP is its capacity to load internet pages quickly and effectively, holding facts usage. This efficiency turned into especially essential within the early days of cellular internet whilst statistics plans had been limited and network speeds have been incredibly gradual.
WAP Protocols
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) relies on specialized protocols for mobile web access:
- WTP (Wireless Transaction Protocol): Manages data exchange, breaking it into packets for efficient wireless transmission.
- WSP (Wireless Session Protocol): Establishes communication sessions between devices and servers, facilitating seamless interaction.
- WAE (Wireless Application Environment): Includes technologies like WML for mobile-friendly content rendering.
- WTLS (Wireless Transport Layer Security): Ensures data encryption, enhancing mobile communication security.
- WDP (Wireless Datagram Protocol): Acts as a bridge between the WAP stack and wireless networks, routing data appropriately.
The Future of Mobile Browsing
As technology advances, mobile browsing is set for exciting developments. Key trends include:
- 5G Speed: 5G networks will deliver lightning-fast speeds and enable AR and VR experiences.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs combine web reach with app functionality for seamless experiences.
- Enhanced User Interfaces: Intuitive interfaces with gestures, voice commands, and AI-driven personalization will simplify navigation.
- Improved Security: Stronger encryption, biometrics, and anti-phishing measures will protect user data.
- WebAssembly (Wasm): Wasm will enable complex web apps and games at near-native speeds.
- AI-Powered Browsing: AI will enhance content recommendations, ad-blocking, and voice search.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Seamless integration between mobile and desktop browsing will become more common.
Conclusion
As we conclude our journey through the world of Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), it’s evident that WAP was a pioneering force in the mobile web landscape. Introduced during a time when mobile phones were just beginning to connect to the internet, WAP provided a gateway to a new digital frontier. It was a crucial stepping stone that laid the foundation for the mobile web we know today.
FAQs About WAP
WAP, which stands for Wireless Application Protocol, is a technical standard that allows mobile devices to access and interact with internet content.
WAP operates by using a set of specialized protocols and languages, including Wireless Markup Language (WML), to convert and optimize web content for mobile devices.
The main components of WAP include WML (Wireless Markup Language), WSP (Wireless Session Protocol), WTP (Wireless Transaction Protocol), WDP (Wireless Datagram Protocol)..
While WAP as it was originally conceived has largely been replaced by more modern mobile technologies, its legacy continues to influence mobile web standards.
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















