A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system, which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs are most common in the bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis).
UTIs are caused by bacteria, usually E. coli. Bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and travel up to the bladder. In some cases, bacteria can also travel to the kidneys.
Introduction
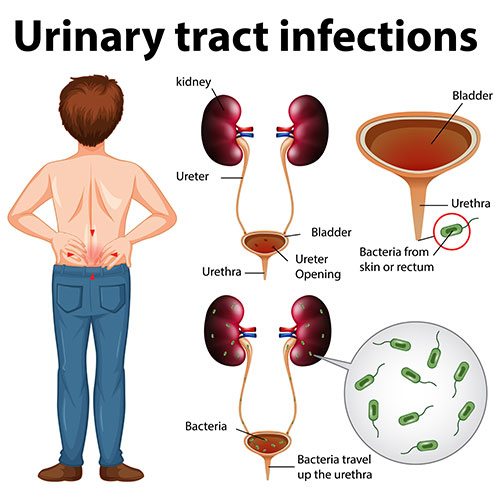
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a common and potentially uncomfortable condition that affects the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs occur when harmful bacteria, typically from the digestive tract, enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing an infection.
Understanding the Urinary Tract
- Kidneys: They filter waste and excess fluid from the blood to form urine.
- Ureters: Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like organ that stores urine.
- Urethra: The tube through which urine exits the body.
How UTIs Develop
UTIs usually begin in the lower urinary tract (the urethra and bladder) but can ascend to the upper urinary tract (the ureters and kidneys) if left untreated. The infection can lead to various symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, and may necessitate medical treatment.
Types of UTIs
- Cystitis: Infection of the bladder, causing frequent urination, a persistent urge to urinate, and discomfort.
- Pyelonephritis: Infection of the kidneys, resulting in fever, chills, back or side pain, and nausea.
- Urethritis: Inflammation of the urethra, often caused by sexually transmitted bacteria or external irritants.
UTIs are more prevalent in women, but men and children can also experience them. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods of UTIs is crucial for effective management and overall well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Bacterial Infections | Escherichia coli (E. coli): The most common cause of UTIs, often found in the gastrointestinal tract. Other bacteria like Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterococcus can also cause infections. |
| Sexual Activity | Sexual intercourse, especially in women, can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract due to the proximity of the urethra to the anus. |
| Urinary Retention or Obstruction | Anything that hinders the complete emptying of the bladder, like kidney stones, an enlarged prostate in men, or congenital abnormalities, can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth and UTIs. |
| Catheter Use | Indwelling catheters provide a pathway for bacteria to enter the urinary tract, making individuals with catheters more susceptible to UTIs. |
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Female Anatomy | Women have a shorter urethra than men, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder and cause infections. |
| Previous UTIs | Having a history of UTIs increases the likelihood of experiencing future infections. |
| Advanced Age | The risk of UTIs increases with age, particularly in postmenopausal women due to hormonal changes. |
| Poor Hygiene | Inadequate personal hygiene, particularly after using the toilet, can introduce bacteria into the urethra. |
| Dehydration | Insufficient fluid intake reduces the frequency of urination, allowing bacteria to multiply in the urinary tract. |
Symptoms and Signs of UTI
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. UTIs can affect any part of the urinary system, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. Here are the common signs indicating a possible UTI:
1. Frequent and Urgent Urination:
If you find yourself needing to urinate more often than usual and feel a sudden, strong urge to urinate, it might be a sign of a UTI.
2. Pain or Burning Sensation During Urination:
Pain, discomfort, or a burning sensation while urinating is a classic symptom of a UTI. It can indicate irritation or inflammation in the urinary tract.
3. Lower Abdominal or Pelvic Pain:
Persistent pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvis, often accompanied by general discomfort, maybe a sign of a UTI affecting the bladder or lower urinary tract.
4. Cloudy, Bloody, or Foul-Smelling Urine:
Changes in the appearance or odor of urine, such as cloudiness, the presence of blood, or a strong, unpleasant smell, can suggest a UTI.
5. Fatigue and Weakness:
UTIs can sometimes cause systemic symptoms like fatigue, weakness, or a feeling of malaise due to the body’s response to the infection.
6. Fever and Chills:
In some cases, especially if the infection has reached the kidneys (pyelonephritis), individuals may experience fever, chills, and even nausea or vomiting.
7. Discomfort in the Lower Back or Sides:
Pain or discomfort in the lower back or sides of the body, indicating a possible kidney infection, should not be ignored.
8. Incontinence or Inability to Urinate:
UTIs can cause a loss of bladder control, resulting in involuntary leakage of urine (incontinence) or difficulty urinating.
9. Sudden Mental Changes (in the Elderly):
In older adults, UTIs can sometimes manifest as sudden confusion, agitation, or other changes in mental function.
Diagnosis and Testing
| Diagnostic Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History and Physical Examination | A healthcare provider gathers information about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, recent activities, and conducts a physical examination, including a pelvic examination for women, to assess signs of infection or other potential issues. |
| Urinalysis | A routine test where a urine sample is analyzed for the presence of white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, and other substances. It provides important clues about a UTI, helping in diagnosis and determining the type of infection. |
| Urine Culture | A laboratory test where a urine sample is placed in a special medium that encourages bacterial growth. This helps identify the specific bacteria causing the UTI and determines the most effective antibiotic for treatment. |
| Imaging Studies | Various imaging techniques such as ultrasound, X-ray, or CT scan may be used to visualize the urinary tract, especially if recurrent or complicated UTIs are suspected, to check for abnormalities, obstructions, or structural issues. |
| Cystoscopy | Involves inserting a thin tube with a camera (cystoscope) through the urethra into the bladder, allowing the doctor to see inside the urinary tract. It’s primarily used when recurring UTIs or other urinary tract issues need a closer examination. |
| Blood Tests | Blood samples may be analyzed to check for elevated white blood cell count or other signs of infection, especially if the UTI has spread to the bloodstream (sepsis). |
| Urodynamic Studies | Specialized tests that evaluate how well the urinary tract is storing and releasing urine. These tests can diagnose issues related to bladder function and help determine the cause of recurrent UTIs or urinary incontinence. |
| Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) | A contrast dye is injected into a vein, and X-rays are taken to visualize the urinary tract. It helps in identifying blockages or abnormalities in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. |
Prevention and Hygiene
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) involves adopting good hygiene practices and making lifestyle choices that reduce the risk of bacterial contamination in the urinary tract. Here are some essential steps to help prevent UTIs:
1. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to promote frequent urination. This helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
2. Maintain Proper Hygiene:
Wipe Front to Back: After using the toilet, always wipe from front to back to prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the urethra, especially in women.
Regular Bathing: Maintain regular personal hygiene, including daily showers, to keep the genital area clean.
3. Urinate Frequently and Completely:
Avoid Holding Urine: Don’t hold your urine for extended periods. Empty your bladder completely when you urinate.
4. Practice Safe Sexual Habits:
Use Protection: Use condoms to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections that can lead to UTIs.
Clean Before and After: Both partners should practice good hygiene before and after sexual activity.
5. Opt for Showers Over Baths:
Avoid Bubble Baths: Bubble baths and strong soaps can irritate the urethra. Choose gentle, unscented products.
Switch to Showers: If possible, opt for showers instead of baths to reduce the risk of introducing bacteria into the urethra.
6. Wear Comfortable Clothing:
Cotton Underwear: Choose breathable, cotton underwear that keeps the genital area dry and prevents the growth of bacteria.
Avoid Tight-Fitting Clothes: Tight clothing can create a warm, moist environment, ideal for bacterial growth.
Treatment and Management
| Treatment and Management | Description |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | – Prescription Medication: Antibiotics are the primary treatment for UTIs. The type and duration of the antibiotic depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection and the severity of the UTI. |
| Pain Relief Medication | – Over-the-Counter (OTC): Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen may help alleviate discomfort and reduce fever associated with UTIs. Ensure you follow proper dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions. |
| Increased Fluid Intake | – Water and Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Increased fluid intake dilutes the urine, making it less concentrated and reducing irritation during urination. Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily, or more if advised by a healthcare provider. |
| Probiotics | – Supplements: Probiotics, like lactobacillus, can help restore healthy bacteria in the urinary tract and prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria. They are available in supplement form or in certain fermented foods like yogurt. |
| Heating Pads | – Warm Compress: Applying a warm heating pad to the lower abdomen or back can help relieve pain and discomfort associated with UTIs. The warmth relaxes the muscles and may alleviate the feeling of urgency and frequency of urination. Ensure the pad is warm, not hot, to avoid burns. |
| Cranberry Products | – Juice or Supplements: Some individuals find relief with cranberry juice or supplements, as they may prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls. However, evidence on their effectiveness varies, and excessive consumption of cranberry products can lead to digestive issues. Consult a healthcare provider before using them. |
| Avoiding Irritants | – Alcohol, Caffeine, and Spicy Foods: Limit or avoid substances that can irritate the bladder, such as alcohol, caffeine, spicy foods, and citrus fruits or juices. These can exacerbate UTI symptoms and discomfort. A bladder-friendly diet can help manage UTI symptoms and promote healing. |
UTI in Special Populations
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) can affect people of all ages and genders, but they may present differently in certain special populations. Here’s how UTIs can manifest in specific groups and considerations for each:
1. UTI in Women:
UTIs are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Women often experience symptoms like frequent urination, burning during urination, pelvic pain, and sometimes, blood in the urine. Prevention involves maintaining proper hygiene, urinating after intercourse, and staying well-hydrated.
2. UTI in Men:
UTIs in men are less common but can be more severe. Men, especially older individuals, may experience symptoms such as a frequent need to urinate, painful urination, lower abdominal pain, or even fever. UTIs in men often signal an underlying issue like an enlarged prostate or kidney stones.
3. UTI in Pregnant Women:
UTIs during pregnancy can be concerning as they increase the risk of complications such as preterm birth or low birth weight. Pregnant women with UTIs may experience frequent urination, urgency, discomfort, and sometimes fever. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to safeguard both the mother and the baby.
4. UTI in Children:
UTIs in children might manifest as irritability, feeding problems, or unexplained fever. In older children, symptoms can include frequent urination, pain during urination, abdominal pain, or bedwetting. Proper hygiene, prompt treatment, and ensuring children drink enough fluids can help prevent and manage UTIs.
5. UTI in the Elderly:
UTIs in the elderly can present with atypical symptoms such as confusion, agitation, or a sudden change in mental status, especially in those with dementia. Other symptoms may include urinary incontinence, a change in mobility, or loss of appetite. Careful monitoring and proactive management are crucial to prevent complications.
6. UTI in Individuals with Diabetes:
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of UTIs due to elevated blood sugar levels that create an ideal environment for bacterial growth. UTIs in individuals with diabetes may present with frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, and fever. Proper blood sugar management and regular check-ups are essential.
7. UTI in Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury (SCI):
SCI can disrupt normal bladder function, leading to increased UTI risk. Individuals with SCI may experience symptoms like fever, autonomic dysreflexia, or cloudy and foul-smelling urine. Proper catheter care, regular follow-ups, and adherence to hygiene practices are crucial in preventing UTIs in this population.
Conclusion
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common yet often uncomfortable conditions that affect people of all ages and genders. The good news is that by understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention techniques, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of UTIs and manage them effectively.
If you suspect a UTI, seeking prompt medical attention and adhering to prescribed treatments, including antibiotics and self-care measures, can aid in a swift recovery and minimize potential complications.
Remember, each person’s experience with UTIs may vary, and it’s important to listen to your body, seek medical advice when needed, and make informed choices to protect your urinary tract health. By doing so, you can enhance your overall well-being and maintain a good quality of life.
Stay informed, practice good hygiene, and prioritize your urinary tract health—it’s a key component of your overall health and vitality.
FAQs
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a bacterial infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. It can cause discomfort and various symptoms related to urination.
UTIs are primarily caused by bacteria, typically Escherichia coli (E. coli), entering the urinary tract. Factors like improper hygiene, sexual activity, urinary retention, or certain health conditions can increase the risk of UTIs.
Common UTI symptoms include frequent and urgent urination, pain or burning during urination, lower abdominal pain, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and in some cases, fever.
UTIs are diagnosed through a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and laboratory tests such as urinalysis and urine culture. Imaging studies may be performed in complex cases.
Read Also
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















