A graphical interface, often called a GUI (pronounced “gooey”), is a visual way for users to interact with a software application or computer system. Unlike text-based interfaces, GUIs use graphical elements such as icons, buttons, menus, and windows to facilitate interaction and make it more convenient for users GUIs have become interactive a intended for most modern software applications, from operating systems, and office suites to the web. on both browsers and mobile applications.
GUI Components
Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) consist of various components that work together to provide an interactive and user-friendly experience. Here are some common GUI components explained in human-written form:
- Windows: These are the primary frames or containers that display content, applications, or documents. Users can resize, move, and interact with multiple windows simultaneously.
- Icons: Graphic symbols or images representing files, applications, or functions. Clicking on icons typically opens or performs the associated action.
- Menus: Drop-down lists or bars that provide users with a list of options and commands. Menus are often organized hierarchically and help users access various functions within an application.
- Toolbars: Rows or columns of icons or buttons containing shortcuts to frequently used functions or tools. They are usually located at the top or sides of the window for quick access.
- Buttons: Clickable elements that perform specific actions when pressed, such as “Save,” “Submit,” or “Cancel.” They are commonly used for user interaction.
- Text Boxes: Areas where users can input text or data, such as search bars, username/password fields, or text editors. Text boxes may include placeholders and validation messages.
History of GUI
Earlier, there was no GUI so people used to interact with the command-line interface(CLI). The CLI was not that friendly to use and the end-user was not familiar with all the commands. So to bridge this gap, GUI was introduced. The main aim of the GUI was to make the applications much more user-friendly. People love it when the task they want to perform gets done easily and in an efficient manner. GUI stresses one of the most important aspects which is ease of use. The basic structure of GUI using implied authority is given in the following diagram
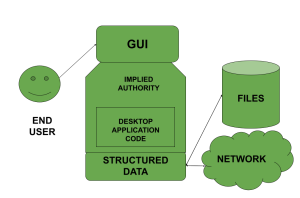
How Does GUI Works
- Windows, icons, and menus are used by a GUI to execute operations including opening, deleting, and moving files. Although a mouse is typically used to browse a GUI operating system, a keyboard can also be used by employing keyboard shortcuts or arrow keys.
- On a GUI system, for instance, you would move the mouse pointer to the program’s icon and double-click it to open the program. To go to the directory holding the program, list the files, and then launch the file using a command line interface, you must be familiar with the commands.
Benefits of GUI
- As mentioned above they are user-friendly i.e. very easy to use.
- A GUI consists of different characteristics such as a Menu, Tabs, Pointers, and many more kinds of stuff.
- The icons on the user interface represent the software or the file or application required on the screen.
- The Graphical User Interface is pretty simple and convenient for beginners to understand.
- It is very intuitive and user-friendly and can be used by anyone.
- End-user need not memorize commands to perform actions in the application.
Limitations of GUI
- Less flexibility: GUIs are designed to be easy to use, which means that they are often limited in their flexibility. Users can only perform the tasks that the developers have pre-programmed into the interface. This can be a problem for users who need to perform more complex tasks or who want to customize the interface to their own needs.
- Can be slow: GUIs can be slower than command-line interfaces (CLIs) because they have to load and render all of the graphical elements. This can be a problem for users who are working on older computers or who are trying to perform time-sensitive tasks.
- Requires more memory: GUIs require more memory than CLIs because they have to store all of the graphical elements. This can be a problem for users who are working on computers with limited memory.
- Can be difficult to learn: GUIs can be difficult to learn for users who are not familiar with them. This is because they often use a variety of icons and menus that can be confusing to new users.
- Can be difficult to use with disabilities: GUIs can be difficult to use for users with disabilities, such as vision or mobility impairments. This is because they often rely on mouse clicks and keyboard shortcuts that may not be accessible to all users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) have revolutionized the way people interact with computers and software by providing a visually intuitive and user-friendly experience. GUIs offer numerous advantages, including ease of use, accessibility for a wide range of users, and the ability to simplify complex tasks. They have become the standard interface for most modern applications and have greatly contributed to the widespread adoption of technology.
FAQs About GUI
A GUI provides a visual interface with icons and menus, while a CLI (Command-Line Interface) relies on text-based commands for interaction.
Common GUI components include windows, icons, menus, buttons, text boxes, and dialog boxes.
GUIs are popular because they are user-friendly, visually intuitive, and make computing accessible to a wide range of users, including those with limited technical expertise.
Yes, many GUIs allow users to customize the appearance, layout, and settings to suit their preferences and needs.
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















