A special economic zone (SEZ) is a geographically designated area within a country where the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are typically created to attract foreign investment and boost economic growth.
Introduction
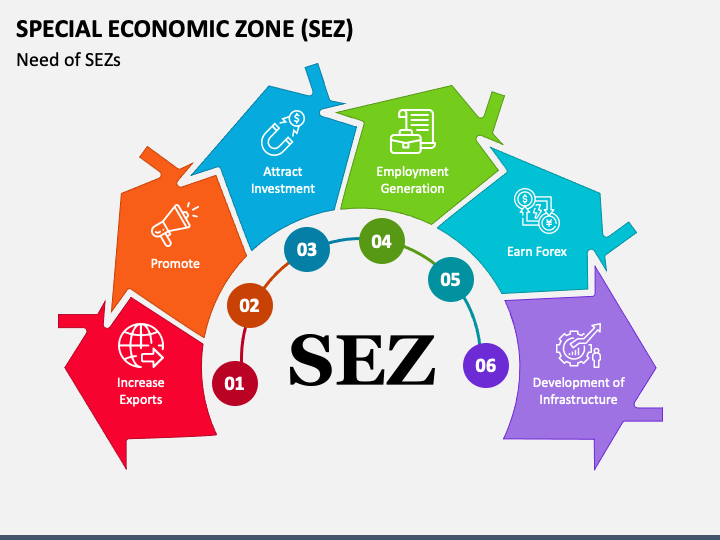
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are designated geographical areas within a country that are subject to specific economic regulations and policies aimed at promoting industrialization, economic growth, and foreign investments. These zones are established to create a favorable business environment that attracts both domestic and foreign investors by offering various incentives and benefits not typically available in the rest of the country.
The concept of SEZs originated to foster economic liberalization and globalization, encouraging international trade and investment. SEZs are considered as tools for economic development, job creation, technology transfer, and skill development. They often feature world-class infrastructure, streamlined procedures, and a conducive business environment that facilitates businesses to flourish.
Objectives of SEZs
The primary objectives of establishing Special Economic Zones include:
- Promoting Investments: Attracting both domestic and foreign investments by providing a business-friendly environment with a range of incentives such as tax breaks, customs benefits, and regulatory simplifications.
- Boosting Exports: Encouraging and facilitating export-oriented industries to enhance a country’s trade balance and competitiveness in the global market.
- Employment Generation: Creating ample employment opportunities by promoting industrialization, which subsequently contributes to poverty reduction and socioeconomic development.
- Technological Advancement: Facilitating technology transfer, research, and development activities by promoting innovation and attracting industries that require advanced technology.
Types of SEZs
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Free Trade Zones (FTZs) | Designated areas with minimal customs intervention where goods can be imported, manufactured, processed, or re-exported easily, often near ports to facilitate trade activities. |
| Export Processing Zones (EPZs) | Zones established to boost exports by providing special incentives and streamlined procedures for manufacturing and exporting goods, focusing on export-oriented industries. |
| Industrial Parks | Concentrated regions of manufacturing and industrial units with specialized infrastructure and facilities to support a variety of industries, promoting industrialization and economic growth. |
| Technology Parks | Zones fostering technology-driven industries, research and development, and innovation by providing an environment conducive to technology transfer and collaboration among research institutions and businesses. |
| Multi-product SEZs | Versatile zones encompassing a wide range of industries, allowing for the development and operation of diverse types of businesses, including manufacturing, IT, biotechnology, and more. |
| Sector-specific SEZs | Dedicated to specific industries or sectors such as pharmaceuticals, textiles, electronics, automotive, or renewable energy, providing a specialized environment that caters to the unique needs of those industries. |
| Agro-based SEZs | Focusing on promoting agro-industries, including food processing, agrochemicals, and related activities, aiming to enhance agricultural productivity, value addition, and market access for agricultural products. |
| Tourism SEZs | Aim to boost the tourism industry by providing incentives for developing tourism-related infrastructure, resorts, entertainment facilities, and services to attract tourists and stimulate economic growth in the tourism sector. |
Global Overview of SEZs
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) have emerged as critical tools for promoting economic growth, attracting investments, and fostering international trade across the globe. While the concept originated in the mid-20th century, SEZs have proliferated extensively since then. This section provides an overview of SEZs worldwide, highlighting their presence, growth, and impact on various economies.
Growth and Spread of SEZs
SEZs have seen remarkable growth globally, with numerous countries establishing and expanding these zones to boost economic development. Some of the key regions experiencing substantial growth in SEZs include:
- Asia: Asia, particularly China and India, has been a leader in establishing and expanding SEZs. China’s rapid industrialization and export-led growth have been significantly supported by its extensive network of SEZs, while India’s SEZ policy has gained traction to promote manufacturing and exports.
- Africa: African countries have increasingly recognized the potential of SEZs to attract foreign investment, stimulate industrialization, and create employment. Nations like Ethiopia, Kenya, and Mauritius have been actively establishing and developing SEZs to drive economic growth.
- Latin America: Latin American countries like Mexico, Brazil, and the Dominican Republic have embraced the SEZ model to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and diversify their economies. SEZs in these regions primarily focus on manufacturing and export-oriented industries.
- Europe: European countries have also utilized SEZs, albeit to a lesser extent than other regions. Countries like Poland, Turkey, and Russia have established SEZs to attract foreign investors and stimulate economic development in specific sectors.
Impact on Economic Growth
The impact of SEZs on economic growth has been substantial, contributing to various aspects of national economies:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): SEZs have successfully attracted FDI by providing favorable investment climates, tax incentives, streamlined procedures, and access to a skilled workforce. This influx of foreign capital fuels economic growth and industrialization.
- Export Growth: SEZs, focusing on export-oriented industries, have significantly boosted a country’s export capabilities. By providing incentives to export-driven companies, SEZs have played a vital role in improving trade balances and enhancing global competitiveness.
- Job Creation: SEZs are potent job creators, generating employment opportunities at various skill levels. This not only alleviates unemployment but also contributes to poverty reduction and social development.
Legislative and Regulatory Framework
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal Foundations | Laws and acts at the national level that provide the legal framework for SEZs. Examples include specific SEZ acts or provisions within broader economic or trade legislation. |
| Policy Objectives | The goals and objectives outlined by the government to guide the establishment and operation of SEZs, focusing on economic development, investment attraction, job creation, and exports. |
| Incentives and Concessions | Special incentives and concessions provided to businesses within SEZs, including tax breaks, customs duties exemptions or reductions, simplified regulatory procedures, and land lease incentives. |
| Governance Structure | The organizational and administrative structure responsible for overseeing and managing SEZs, including government agencies, development authorities, and regulatory bodies tasked with SEZ oversight. |
| Investment Approval and Compliance | Procedures and requirements for obtaining approval to invest and operate within an SEZ, as well as compliance standards that businesses must adhere to, ensuring adherence to SEZ rules and regulations. |
| Land Acquisition and Allocation | Processes and policies related to acquiring and allocating land for SEZ development, including land acquisition laws, land lease terms, compensation mechanisms, and rules governing land usage within SEZs. |
| Environmental and Social Regulations | Regulations ensuring adherence to environmental and social standards, promoting sustainable development within SEZs, and mitigating potential negative impacts on the environment and local communities. |
| Labor Laws and Employment Regulations | Employment laws, regulations, and labor standards applicable to workers within SEZs, addressing aspects like wages, working conditions, safety regulations, and labor rights, ensuring fair treatment of the workforce. |
Establishing and Operating an SEZ
Establishing and operating a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) involves a comprehensive process that requires careful planning, compliance with regulatory frameworks, and strategic decision-making. This section outlines the key steps and considerations involved in setting up and managing an SEZ.
1. Feasibility Study and Market Analysis: Conduct a thorough feasibility study and market analysis to assess the viability and potential of the proposed SEZ. Evaluate factors such as location, market demand, infrastructure availability, and competitive landscape.
2. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with the specific legal and regulatory requirements governing SEZs in the target country. Ensure compliance with laws related to investments, land acquisition, environmental regulations, and labor laws.
3. Site Selection and Planning: Identify an appropriate location for the SEZ, considering proximity to transportation hubs, availability of utilities, and alignment with the objectives of the SEZ. Develop a master plan outlining the layout, infrastructure, and zoning of the SEZ.
- Application and Approvals: Submit a formal application to the relevant government authorities for approval to establish the SEZ. Provide a detailed proposal outlining the SEZ’s objectives, expected economic impact, investment plan, and job creation potential.
- Infrastructure Development: Develop necessary infrastructure within the SEZ, including roads, power supply, water and sanitation facilities, and communication networks. Infrastructure should align with the needs of the target industries and support seamless operations.
- Incentives and Concessions: Negotiate with government authorities for attractive incentives and concessions for businesses operating within the SEZ. These incentives may include tax breaks, customs benefits, and streamlined regulatory procedures to attract investments.
Investments and Economic Impact
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Investments Attraction | SEZs act as magnets for domestic and foreign investments by offering incentives such as tax breaks, customs benefits, simplified regulatory processes, and other attractive investment conditions. |
| Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) | Attracting FDI is a significant impact of SEZs, contributing to increased capital inflow, job creation, technology transfer, and overall economic growth. |
| Domestic Investments | SEZs encourage local businesses to invest and expand operations within the zone, fostering industrial growth, creating employment opportunities, and boosting the nation’s economic landscape. |
| Export Promotion | By focusing on export-oriented industries, SEZs significantly contribute to boosting a country’s export capabilities, improving trade balance, and increasing foreign exchange earnings, leading to a positive economic impact. |
| Job Creation | SEZs are significant job generators, creating employment opportunities across various skill levels, thus reducing unemployment and contributing to social and economic development. |
| Technology Transfer and Innovation | SEZs facilitate technology transfer and innovation by attracting technology-driven industries, promoting research and development activities, and fostering collaboration between businesses and research institutions. |
| Industrial Diversification | SEZs encourage diversification by supporting a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, services, technology, and research, leading to a balanced and robust economic ecosystem. |
| Economic Growth | SEZs stimulate overall economic growth by promoting industrialization, attracting investments, generating employment, enhancing productivity, and fostering innovation, all of which contribute to a nation’s economic prosperity. |
Conclusion
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) have emerged as powerful instruments for promoting economic growth, attracting investments, fostering industrialization, and encouraging international trade. This conclusion highlights the key aspects and benefits of SEZs and emphasizes their vital role in shaping modern economies.
FAQs
A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a designated geographic area within a country that operates under specific economic regulations and policies aimed at promoting investment, economic growth, exports, and job creation. SEZs offer various incentives to attract businesses and investors.
The primary objectives of establishing SEZs include attracting foreign and domestic investments, promoting exports, creating employment opportunities, facilitating technology transfer, and boosting infrastructure development in a focused and controlled environment.
Incentives in SEZs often include tax exemptions or reductions, customs duty benefits, simplified regulatory procedures, infrastructure support, and relaxed labor and environmental regulations. These incentives vary based on the specific policies of the country hosting the SEZ.
SEZs contribute to economic growth by attracting investments, promoting exports, creating jobs, facilitating technology transfer, fostering industrialization, and developing infrastructure. These factors collectively stimulate economic activity and drive overall economic prosperity.
Read Also
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















