A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs can be wired or wireless, and they can be used to share resources such as printers, files, and internet access.
Introduction to LAN
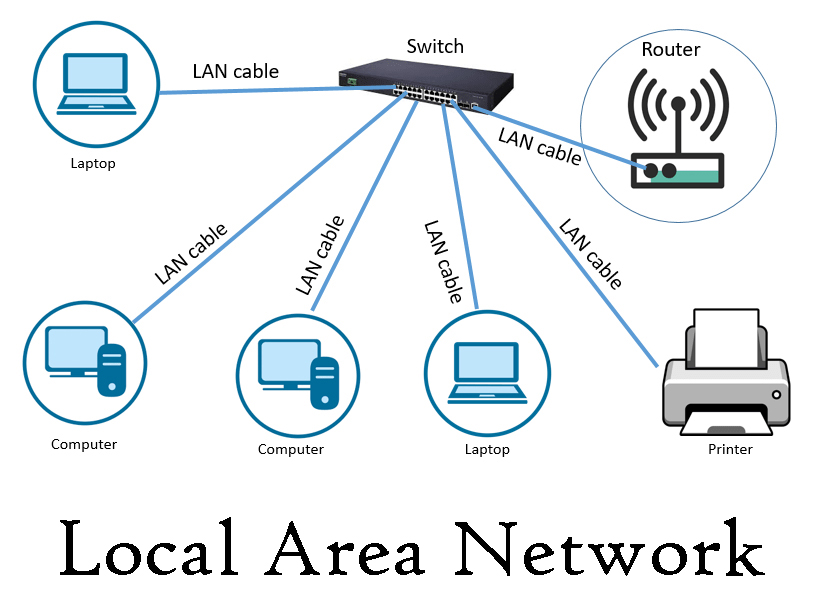
In the vast landscape of modern communication and technology, Local Area Networks (LANs) stand as the unsung heroes that power our interconnected world. From homes to offices, schools to cafes, LANs silently facilitate the flow of information, enabling seamless communication and sharing within a confined geographical area. In this introductory section, we embark on a journey to unravel the essence of LANs, understanding their significance, components, and the role they play in our daily lives.
Defining the Local Area Network (LAN): At its core, a Local Area Network (LAN) is a network of interconnected devices within a limited geographic area. These devices, which can range from computers and printers to smartphones and IoT devices, are linked together to enable data sharing, resource access, and collaborative work.
The LAN’s Playground: From Home to Workplace: LANs are omnipresent in our surroundings, often operating inconspicuously. They form the digital backbone of homes, connecting family members to each other and to the world. In workplaces, LANs foster productivity, allowing colleagues to collaborate on projects, share resources, and access central databases.
How LANs Work
| No. | LAN Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | LAN Architecture | – Client-server architecture: Devices (clients) connect to a central server for coordinated network activities. |
| – Peer-to-peer architecture: Devices communicate directly without a dedicated server in smaller setups. | ||
| 2. | Networking Devices | – Switches: Manage data traffic, direct information to the right recipient, create dedicated communication paths. |
| – Routers: Connect different LANs, determine efficient paths for data transmission between networks. | ||
| 3. | Communication Protocols | – Ethernet: Common LAN protocol for data packet transmission via Ethernet cables. |
| – Wi-Fi (Wireless LAN): Uses Wi-Fi protocols (e.g., IEEE 802.11) for wireless connections, enabled by access points. | ||
| 4. | Data Transmission | – Data is divided into packets containing sender and recipient addresses for accurate delivery. |
| – Devices send packets, switches and access points receive and analyze packet addresses to determine the route. |
Types of LAN Topologies
| No. | LAN Topology | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Star Topology | – Central hub or switch connects all devices. |
| – Devices communicate with the hub/switch, which manages traffic. | ||
| – High reliability; failure of one device doesn’t affect others. | ||
| – Easy to install and manage. | ||
| 2. | Bus Topology | – Devices connected to a central cable (bus). |
| – Single point of failure (if the cable breaks, the network goes down). | ||
| – Data transmission can be affected by heavy traffic. | ||
| 3. | Ring Topology | – Devices connected in a closed loop. |
| – Data travels in one direction, passing through each device. | ||
| – Failure of one device can disrupt the entire network. | ||
| – Relatively less common due to its susceptibility to failures. | ||
| 4. | Mesh Topology | – Every device connects to every other device. |
| – High redundancy and fault tolerance; network stays functional even with multiple failures. | ||
| – Complex to implement and manage, costly due to numerous connections. |
LAN Components and Infrastructure
| No. | LAN Components and Infrastructure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Network Devices | – Switches: Manage data traffic, direct data to the appropriate recipient, create dedicated paths. |
| – Routers: Connect different LANs or segments, determine the best path for data to travel. | ||
| – Hubs: Basic networking devices that connect multiple devices in a network. | ||
| – Access Points: Enable wireless connectivity in wireless LANs (Wi-Fi). | ||
| 2. | Ethernet Cables | – Used for wired connections, transmitting data packets between devices and switches. |
| 3. | Wireless Connectivity | – Wireless LANs (Wi-Fi) enable devices to connect without physical cables, using radio waves. |
| – Access points provide wireless coverage areas and facilitate device connections. | ||
| 6. | Data Servers | – Centralized devices that store and manage data, making it accessible to other devices in the LAN. |
| 7. | Clients | – Devices (computers, smartphones, IoT devices) that connect to the LAN to access resources and data. |
LAN Setup and Configuration
Hardware Requirements:
- Router: The central device that manages network traffic and provides connectivity to devices.
- Ethernet Cables: Used to connect devices to the router via Ethernet ports.
- Switch (Optional): Expands the number of available Ethernet ports for wired connections.
- Wireless Access Points (WAPs) (Optional): For wireless connectivity in addition to wired connections.
- Computers and Devices: Desktops, laptops, smartphones, and printers to be connected to the LAN.
Step-by-Step Configuration:
- Connect the Router:
- Plug the router into a power source and connect it to your modem (if separate).
- Use an Ethernet cable to connect your computer to the router’s LAN port.
- Access Router Settings:
- Open a web browser and enter the router’s IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) in the address bar.
- Log in using the router’s default username and password (check the router manual).
- Change Admin Password:
- Update the default admin password to enhance security.
- Configure LAN Settings:
- Assign a static IP address to the router.
- Set the LAN subnet mask (often 255.255.255.0).
LAN Security Measures
| No. | LAN Security Measures | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Firewalls | – Network security devices that monitor and filter incoming and outgoing network traffic based on defined rules. |
| 2. | Encryption | – Data encryption (e.g., WPA3 for Wi-Fi) ensures that data transmitted over the network is secure and private. |
| 3. | Access Control | – Implement user authentication and authorization mechanisms to control who can access the LAN resources. |
| 4. | Virtual LANs (VLANs) | – Segmentation of the network into smaller virtual LANs to enhance security and manage access more effectively. |
| 5. | Intrusion Detection | – Systems that detect and alert administrators to potential unauthorized access attempts or malicious activity. |
| 6. | Network Monitoring | – Continuous monitoring of network traffic to identify unusual patterns or behaviors that might indicate threats. |
LAN vs. WAN: Understanding the Difference
| No. | LAN vs. WAN: Understanding the Difference | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Definition | – LAN (Local Area Network): Connects devices within a limited geographic area, like a home or office. |
| – WAN (Wide Area Network): Spans larger geographical areas, often connecting LANs across different cities or countries. | ||
| 2. | Size and Coverage | – LANs cover small areas, typically within a single building or a few adjacent buildings. |
| – WANs cover larger areas, often spanning cities, countries, or even continents. | ||
| 3. | Ownership and Control | – LANs are usually owned and controlled by a single organization or individual. |
| – WANs may involve multiple organizations or service providers collaborating for connectivity. | ||
| 4. | Data Transfer Speed | – LANs generally offer higher data transfer speeds due to shorter distances and dedicated connections. |
| – WANs may have slower speeds due to longer distances and reliance on public networks. | ||
| 5. | Hardware and Connectivity | – LANs primarily use Ethernet cables for wired connections and Wi-Fi for wireless connections. |
| – WANs rely on various technologies, including leased lines, fiber optics, and satellite connections. |
LAN Applications and Use Cases
Local Area Networks (LANs) are the backbone of modern connectivity, enabling seamless communication and data sharing within a limited geographic area. This section explores various applications and use cases of LANs, showcasing their versatility and impact on different settings.
- Home Networking:
- Connecting devices like computers, smartphones, and smart TVs for sharing resources and internet access.
- Sharing files, printers, and multimedia content among family members.
- Gaming and streaming experiences with low latency.
- Small Offices and Businesses:
- Centralized file storage and sharing to enhance collaboration among employees.
- Sharing networked printers and scanners for efficient document management.
- VoIP and video conferencing for cost-effective communication.
- Educational Institutions:
- Providing internet access and e-learning resources to students and teachers.
- Facilitating communication among students, faculty, and staff members.
- Managing access to online databases and educational materials.
- Healthcare Facilities:
- Sharing patient records and medical data securely among healthcare professionals.
- Enabling real-time communication for doctors, nurses, and administrative staff.
- Accessing and updating electronic health records efficiently.
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of our digital world, where data flows seamlessly and communication transcends borders, Local Area Networks (LANs) stand as the unshakable foundation upon which modern connectivity is built. As we conclude our exploration of LANs, it becomes clear that their significance reverberates through homes, workplaces, and educational institutions, shaping how we interact, share information, and collaborate.
FAQs
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network of interconnected devices within a confined geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. It facilitates data sharing, resource access, and communication among devices.
LANs consist of various components, including switches, routers, hubs, access points, Ethernet cables, wireless connectivity, network interface cards (NICs), and network media.
Switches manage data traffic within a LAN, directing information to the appropriate recipient and creating dedicated communication paths. Routers connect different LANs, determining the most efficient path for data to travel.
LANs cover a limited geographic area, such as a building or a group of nearby buildings. WANs, on the other hand, span larger geographical areas, connecting LANs across cities, countries, or continents.
Read Also
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















