What Is Emotional Intelligence
Salovey and Mayer in 1990 came up with the first published attempt in trying to define the term “EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE.” They defined emotional intelligence (EI) as “the ability to monitor one’s own and other feelings and emotions, to discriminate among them, and to use this information to guide one’s thinking and actions.”
Emotional intelligence refers to a person’s capability to manage and control their emotions and possess the ability to control others’ emotions. In other words, they can influence the feelings of other people also. Emotionally intelligent people are highly influential and eloquent with their use of words.
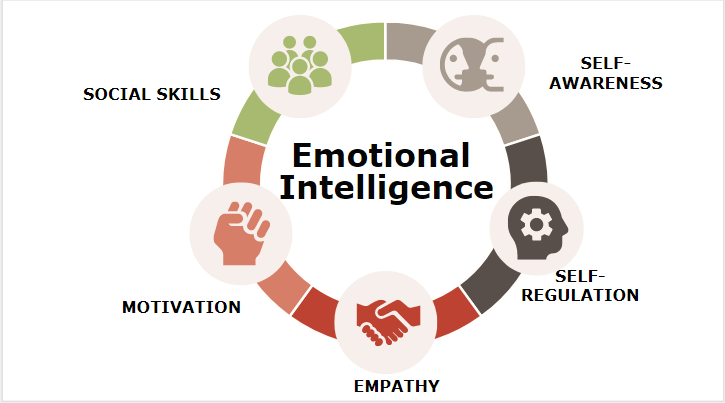
Attributes of EI
Mindfulness – Recognizing one’s own feelings and how they influence our musings and conduct, knowing our qualities and shortcomings, and having fearlessness.
Self-administration – Being ready to control hasty sentiments and practices, deal with our feelings in sound ways, stepping up, finishing on duties, and adjust to evolving conditions. All-consuming purpose balance is significant.
Social mindfulness – One can comprehend the feelings, needs, and worries of others, get enthusiastic prompts, feel-good socially, and perceive the force elements in a gathering or association.
Relationship Management– Knowing how to create and keep up great connections, obviously, rouse and impact others, function admirably in a group, and oversee strife.
Models Of Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Emotional intelligence is often estimated with the help of the Emotional Intelligence quotient (EQ), which represents the capacity or ability of an individual to understand, evaluate, and eventually handle others’ emotions along with themselves. 3 main EI models have been discovered to date, namely:
- Model-based on Trait
- Models based on Ability
- Mixed models

The Trait Emotional Intelligence model
Trait emotional intelligence or Trait emotional self viability alludes to “a star grouping or conduct self-recognition concerning peoples’ capacity to perceive, measure and use enthusiastic loaded data” where the characteristic EI ought to be estimated inside the system of a peoples’ character.
Emotional intelligence model based on the ability
This model upholds feelings as indispensable data sources that empower an individual to utilize the social condition. As per the model, a person’s capacity to handle enthusiastic data shifts starting with one individual onto the next, and certain versatile practices show themselves in this capacity. The model thus goes further to propose four ability types that include
- Understanding of emotions
- Using of emotion
- Perceiving emotions and
- Initiating the emotions
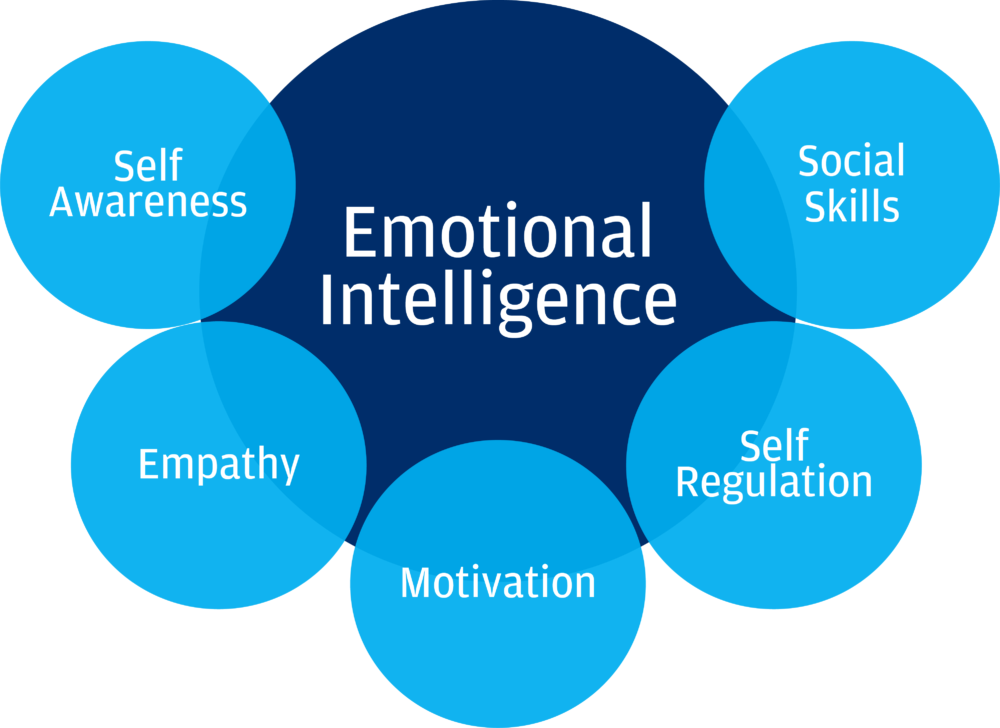
Mixed models of emotional intelligence
It includes Goleman’s Emotional Competencies and Bar-On’s emotional-social intelligence model.
- The emotional competencies (Goleman) model– This is a model introduced by Daniel Goleman, who portrays EI as a combination of various skills and competencies that strengthen managerial performance. Goleman developed 4 outlines for emotional intelligence, which are Self-awareness, self-management, social-awareness, relationship-management.
- The Bar-On model of emotional-social intelligence (ESI) was developed by Reuven Bar-On, a psychologist. He defined EI as “involving the practical understanding of others including oneself and being able to relate well with people and develop the ability to deal effectively with the environmental dynamics and adapt and cope with them. According to Bar-On, emotional intelligence is formed over time and improved by training therapy and programming.
Importance of Emotional Intelligence
- Better Communication: Emotional Intelligence helps to foster a healthy relationship with others.
- For Decision making: EI helps in perceiving such feelings that are irrelevant to a particular issue and not permitting them to be compelling to the conclusive outcome.
- For leading others: Leaders with high EI have solid mindfulness of their feelings to more readily impart, impact, and rouse others to make a move.
- Stress Management: It empowers one to handle emotions in anxiety-provoking situations, thus maintaining physical and mental well-being.
- In personal life- EI makes one more adaptable, empathetic, and clear in expression.
- Accepting change: An Emotionally Intelligent person is more hopeful of adapting to new things, take risks, and face new hurdles without fear. Thus helping in finding innovative solutions to different problems.
- EI in professional life: At the workplace, the capacity to “practice clear and savvy instinct in circumstances that the position’s job presents” exclusively rely upon the emotional intelligence representatives have. It includes the ability to deal with their own motivations, adapt to change, viably speak with others, and take care of issues and having the option to utilize humor to defuse a strained circumstance. Such representatives can understand others, are idealistic, notwithstanding downturns, and successfully settling client grievances. Accordingly, EI assumes an indispensable part in isolating top entertainers from feeble ones at the workplace.

How to Improve Emotional Intelligence?
- Without anyone else assessing oneself, one can know one’s feelings and responses to various circumstances.
- By watching others, one can fathom the sentiments of others.
- By improving one’s demeanor, one can convey better.
- By investigating the effect of one’s activity over others, one can calibrate the activities.
Conclusion
Concerning to adjust our personal and professional life, emotional intelligence matters similarly to intellectual capacity. EI helps individuals build more grounded connections, prevail at work, and accomplish their professional and individual objectives, making it not quite the same as different perspectives. Although EI is generally new in psychological research, it is a field that ought not to be overlooked because it leads to the overall development of an individual.




















