BCC (Blind Carbon Copy) is an email functionality that empowers the sender to discreetly share an email with supplementary recipients, all while safeguarding their email addresses from the main addressees. This feature proves especially handy in scenarios where the sender aims to uphold the confidentiality of these additional recipients or seeks to thwart the forwarding or replying of the email to them. For instance, a supervisor might send an email to the project team while employing BCC to loop in a higher-level executive or the HR department. This way, the manager can relay updates or concerns to these undisclosed parties without alerting the team members.
Table of Content

How BCC Works
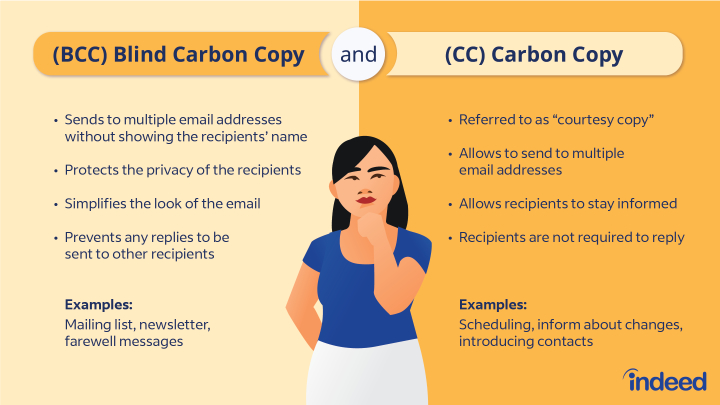
- Blind Carbon Copy (BCC) is an email feature that allows you to send a message to multiple recipients without revealing their email addresses to each other. When you use the BCC field, recipients can’t see who else received the email. It’s useful for maintaining privacy and preventing a long list of email addresses from being exposed to all recipients.

- Adding BCC Recipients: When composing an email, you’ll typically see fields like “To,” “CC” (Carbon Copy), and “BCC.” To use BCC, you enter the email addresses of the recipients you want to hide in the “BCC” field.
- Recipient Visibility: Recipients in the “To” and “CC” fields can see each other’s email addresses. However, recipients in the “BCC” field are hidden from everyone else. This helps prevent accidental sharing of email addresses or spamming.
- Replies: When someone replies to an email sent using BCC, their reply only goes to the sender, not to other recipients. This maintains individual privacy.
- Why Use BCC: BCC is often used for professional communications, like sending newsletters, announcements, or invitations to a large group. It’s also helpful when sending emails to multiple parties who may not know each other or when you want to keep recipients’ identities private.
- Respecting Privacy: Using BCC shows consideration for recipients’ privacy and can help prevent misuse of their email addresses.
Difference between BCC and CC (Carbon Copy)
Risks and Consequences of Misusing BCC
Misusing BCC (Blind Carbon Copy) in email communication can have several potential risks and consequences, including
- Breach of Trust: If the BCC feature is used to hide information from the primary recipients, it can lead to a breach of trust and damage relationships between the sender and the primary recipients.
- Violation of Privacy: If the BCC feature is used to share sensitive or confidential information without the recipient’s knowledge or consent, it can violate their privacy rights.
- Legal Implications: Misusing BCC to share confidential or sensitive information can have legal implications, especially if it violates privacy or confidentiality agreements or if the information falls under regulated categories such as financial or medical information.
- Reputational Damage: Misusing BCC can lead to reputational damage, particularly if it results in a breach of trust, a privacy violation, or legal action.
- Loss of Productivity: Misusing BCC can result in unnecessary emails, confusion, and wasted time, leading to a loss of productivity for the sender and the recipients.
Best Practices for Using BCC
When using the Blind Carbon Copy (BCC) field in emails, there are several best practices to consider for effective and considerate communication. First and foremost, always prioritize recipients’ privacy and respect their personal information.If you’re sending an email to a group of people who might not know each other, or if you’re dealing with sensitive content, it’s wise to use the BCC field. This prevents recipients from seeing each other’s email addresses, reducing the potential for misuse or spam
In professional settings, such as work-related announcements or business communications, using BCC showcases professionalism by safeguarding contact details and avoiding the accidental sharing of addresses. This is particularly important when dealing with clients, colleagues, or partners. For newsletters or updates sent to a mailing list, make a practice of employing BCC. This maintains the privacy of subscribers’ email addresses, enhancing trust and discouraging email harvesting.
BCC Etiquette and Communication Efficiency
Utilizing Blind Carbon Copy (BCC) in email communications is not just about concealing recipients’ email addresses; it also plays a significant role in maintaining proper etiquette and enhancing communication efficiency. BCC etiquette encompasses a set of considerations that respect recipients’ privacy while streamlining interactions. When sending group emails to individuals who might not be acquainted, using BCC helps safeguard their email addresses, preventing potential discomfort or misuse of personal information. This is particularly important in professional scenarios, where maintaining a professional image and adhering to data protection norms are paramount
Conclusion
BCC (Blind Carbon Copy) is a useful feature in email communication that allows the sender to include additional recipients without revealing their email addresses to the primary recipients. While BCC can help maintain privacy and confidentiality, it should be used judiciously and in accordance with ethical considerations to avoid potential risks and consequences.
FAQs About BCC
BCC stands for “Blind Carbon Copy.” It’s an email feature that allows you to send a copy of an email to additional recipients without revealing their email addresses to the main recipients
CC (Carbon Copy) allows recipients to see the email addresses of all other recipients, while BCC keeps those addresses hidden from all recipients except the sender.
CC is used when you want to keep the identities of additional recipients confidential or prevent primary recipients from replying to or forwarding the email to BCC recipients.
BCC protects recipient privacy, reduces email clutter, prevents “reply all” mishaps, and allows you to discreetly share information with specific individuals.
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture




















