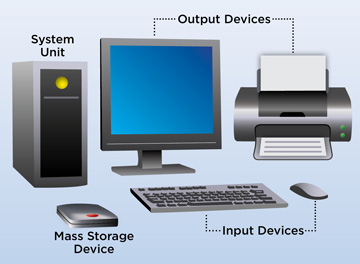
A computer is a programmable electronic device that accepts raw data as input and processes it with a set of instructions (a program) to produce the result as output. It renders output just after performing mathematical and logical operations and can save the output for future use. It can process numerical as well as non-numerical calculations. The term “computer” is derived from the Latin word “computare” which means to calculate.
Computers are categorized into types based on various criteria. When considering size, computers can be grouped into five main types
- Micro Computer
- Mini Computer
- Mainframe Computer
- Super Computer
- Workstations
1. Micro Computer:
A microcomputer is a type of computer designed for use by a single person. It may not have the same level of speed and storage space as larger computers. Instead of complex processors, microcomputers use microprocessors as their brains. In fact, the very first microcomputers were created using 8-bit microprocessor chips.
You’ve likely encountered microcomputers in your daily life. Laptops and desktop computers are common examples. Even devices like personal digital assistants (PDAs), tablets, and smartphones fall under this category. Microcomputers are built with everyday tasks in mind. They’re perfect for activities such as browsing the web, searching for information, using the internet, working with MS Office applications, and connecting through social media platforms. Their user-friendly design aims to make these tasks simple and accessible for everyone.
2. Mini Computer:
Mini-computers, often referred to as “Midrange Computers,” stand apart from their microcomputer counterparts. Unlike microcomputers, which are tailored for individual use, mini-computers are strategically engineered to cater to multiple users concurrently. This characteristic positions them as multi-user systems, proficient in accommodating numerous users simultaneously.
One of the primary distinctions of mini-computers is their suitability for small businesses and firms. These compact yet powerful machines are ideally crafted to bolster the operations of such enterprises. While microcomputers are geared towards individual tasks, mini-computers excel in shared environments where several users need to collaborate on tasks or access resources concurrently.
In practice, mini-computers often find their niche within distinct departments of a company. Take, for instance, the admission department of a university. This segment can harness the capabilities of a mini-computer to streamline and supervise the intricate admission process. By leveraging its multi-user capacity, various staff members can work harmoniously on different aspects of admissions, such as application review, document processing, and student communication.
3. Mainframe Computer:
Mainframe computers are like versatile team players, capable of hosting thousands of users all at once. These tough machines thrive in big businesses and government setups, working hard behind the scenes to make sure important operations run smoothly by efficiently handling huge amounts of data.
Imagine these mainframes as key players in the fields of finance, education, and insurance. Think of banks, relying on these strong systems to carefully organize and process all the information about their customers. Universities also count on mainframes to keep track of student records and handle all the behind-the-scenes administrative tasks. And let’s not forget insurance companies – they put these mainframes to work to protect and manage the data related to their policyholders. In a way, mainframe computers are like the silent heroes in the background, supporting the everyday workings of industries we rely on. They may not grab the spotlight, but they’re the dependable force that keeps everything ticking in our modern world….
4. Super Computer:
Supercomputers represent the zenith of computing prowess. These extraordinary machines, while being the costliest and swiftest in the computing domain, possess unparalleled capabilities. With massive storage capacities and lightning-fast processing speeds, they effortlessly carry out millions of instructions each second.
The true allure of supercomputers resides in their precision. They are meticulously engineered for specific purposes, finely tuned to excel in particular tasks. This specialized nature renders them invaluable for applications requiring immense computational power, particularly in scientific and engineering domains. From tackling monumental numerical challenges to unravelling intricacies in fields like electronics, petroleum engineering, weather forecasting, medicine, and space exploration, supercomputers prove irreplaceable.
Let’s consider NASA’s pursuits in space exploration. When launching satellites into the cosmic expanse and adeptly supervising and guiding them through the immense unknown, NASA relies on supercomputers. These high-powered systems aid in analyzing intricate data, simulating complex cosmic phenomena, and plotting optimal courses for interstellar journeys. This harmonious fusion of computational potency and scientific inquiry stands as a testament to the profound influence of supercomputers.
5. Work stations:
A workstation is a type of computer crafted for individual use. It looks quite similar to a personal computer, but it’s equipped with a more robust microprocessor and a top-tier monitor compared to standard microcomputers. Placed between personal computers and minicomputers concerning storage and speed, workstations bring an added level of power to the table.
These workstations shine brightest in specific roles like desktop publishing, software development, and engineering designs. Picture them as the reliable tools professionals turn to when facing intricate challenges. Whether it’s creating detailed layouts, coding innovative software, or fashioning elaborate engineering blueprints, workstations are custom-built for these intricate tasks.
In its essence, a workstation can be likened to the heavy-duty machinery of the computing realm. It offers amplified capabilities, ready to tackle demanding projects head-on. As the unsung hero, workstations enable high-quality designs, intricate coding, and groundbreaking engineering feats – all of which help shape the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
Benefits of Using a Computer:
- Increases your productivity: A computer increases your productivity. For example, after having a basic understanding of a word processor, you can create, edit, store, and print the documents easily and quickly.
- Connects to the Internet: It connects you to the internet that allows you to send emails, browse content, gain information, use social media platforms, and more. By connecting to the internet, you can also connect to your long-distance friends and family members.
- Storage: A computer allows you to store a large amount of information, e.g., you can store your projects, ebooks, documents, movies, pictures, songs, and more.
- Organized Data and Information: It not only allows you to store data but also enables you to organize your data. For example, you can create different folders to store different data and information and thus can search for information easily and quickly.
- Improves your abilities: It helps write good English if you are not good at spelling and grammar. Similarly, if you are not good at math, and don’t have a great memory, you can use a computer to perform calculations and store the results.
- Assist the physically challenged: It can be used to help the physically challenged, e.g., Stephen Hawking, who was not able to speak used computer to speak. It also can be used to help blind people by installing special software to read what is on the screen.
- Keeps you entertained: You can use the computer to listen to songs, watch movies, play games and more.
FAQ About Computer
A computer is an electronic device that processes data using instructions to perform various tasks. It consists of hardware components like a central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage, input/output devices, and software.
The main types of computers include microcomputers (personal computers), minicomputers, mainframes, and supercomputers. These categories differ in terms of size, processing power, and usage.
An operating system (OS) is software that manages a computer’s hardware and provides a user interface for interacting with the computer. Examples include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Storage capacity refers to the amount of data a computer can store. It’s measured in units like bytes, kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), terabytes (TB), and more.
Hardware refers to the physical components of a computer, such as the CPU, memory, keyboard, and monitor. Software, on the other hand, includes programs, applications, and the operating system that run on the hardware.
Related posts:
- AMC Full Form: Benefits, Components, Needs, Advantage
- ORS Full Form: Dehydration, Myths, Flavors, Varieties & Facts
- PCC Full Form: Importance, Types, Application Process
- PAN Full Form: Legal Provisions, Regulations,
- BRB Full Form: Productive, Routine, Distractions
- MCD Full From: Introduction, Responsibility, Challenges
- CT Scan Full Form: Scans, price, Advantages
- USA Full Form: History, Economics,Technology, culture