Table Of Content:
Introduction Of MCD

In India, the city of Delhi was operated and administered by the Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD), a local governmental body. In its area of duty, it was crucial in maintaining and providing basic public services. One of the greatest municipal corporations in the world, the MCD was a vital component of Delhi’s local government system.
Originally established in 1958 under the Delhi Municipal Corporation Act, the MCD had jurisdiction over a vast area and population, covering various aspects of urban development and civic amenities. Its primary responsibilities included:
- Urban Planning and Development: The MCD was responsible for regulating and managing urban development, including town planning, zoning regulations, and building approvals. It played a significant role in shaping the city’s growth and infrastructure.
- Public Health and Sanitation: The MCD was tasked with ensuring public health and hygiene within the city. This included maintaining sanitation, waste management, and controlling the spread of diseases.
- Roads and Infrastructure: The corporation was responsible for the construction, maintenance, and repair of roads, bridges, and other vital infrastructure to facilitate smooth transportation and connectivity.
- Education and Health Services: The MCD managed a network of schools, dispensaries, and health centers to provide basic education and healthcare services to the residents of Delhi.
- Parks and Recreational Facilities: The MCD maintained parks, gardens, and recreational spaces, contributing to the quality of life for the city’s inhabitants.
- Local Governance and Civic Services: It conducted local elections, collected property taxes, issued licenses, and provided various civic services to the citizens.
The Structure of MCD: Divisions and Departments
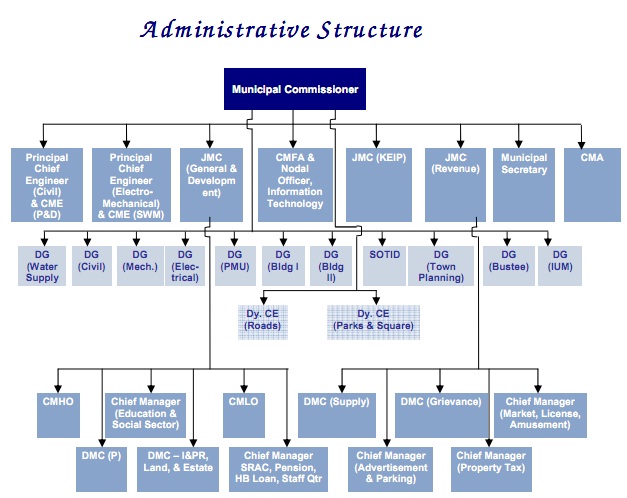
The Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) is the governing body for the National Capital Territory of Delhi, India. It is divided into six divisions, each with its own set of departments. The divisions are:
- Central Division: This division covers the central part of Delhi, including Connaught Place, Jantar Mantar, and the Red Fort.
- North Division: This division covers the northern part of Delhi, including Karol Bagh, Chandni Chowk, and the India Gate.
- Northeast Division: This division covers the northeastern part of Delhi, including Rohini, Pitampura, and Shalimar Bagh.
- South Division: This division covers the southern part of Delhi, including Greater Kailash, Vasant Vihar, and Saket.
- Southeast Division: This division covers the southeastern part of Delhi, including Dwarka, Najafgarh, and Tughlakabad.
- West Division: This division covers the western part of Delhi, including Punjabi Bagh, Tilak Nagar, and Janakpuri.
Each division has a number of departments, which are responsible for different aspects of municipal governance. Some of the major departments in each division include:
- Engineering Department: This department is responsible for maintaining roads, bridges, and other infrastructure.
- Health Department: This department is responsible for providing healthcare services to the public.
- Education Department: This department is responsible for providing education services to the public.
- Sanitation Department: This department is responsible for collecting garbage and maintaining cleanliness in the city.
- Parks and Gardens Department: This department is responsible for maintaining parks and gardens in the city.
Key Responsibilities of MCD
The Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) is the governing body for the National Capital Territory of Delhi, India. It has a wide range of responsibilities, including:
- Providing basic infrastructure: The MCD is responsible for maintaining roads, bridges, and other infrastructure in Delhi. It also provides water supply, sewerage, and drainage services.
- Providing healthcare services: The MCD runs a network of hospitals and clinics across Delhi. It also provides immunization and other preventive healthcare services.
- Providing education services: The MCD runs a network of primary and secondary schools across Delhi. It also provides scholarships and other educational support to students.
- Maintaining cleanliness: The MCD is responsible for collecting garbage and maintaining cleanliness in Delhi. It also operates a fleet of street sweepers and cleaning crews.
- Enforcing laws: The MCD is responsible for enforcing laws related to public health, safety, and sanitation. It also issues licenses and permits for businesses and other organizations.
- Planning for the future: The MCD is responsible for planning for the future development of Delhi. It prepares master plans for the city and implements projects to improve infrastructure and services.
Challenges Faced by MCD
The Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) has faced numerous challenges over the years in its efforts to provide efficient governance and essential services to the city’s residents. Some of the key challenges include:
- Rapid Urbanization and Population Growth:
Delhi’s population growth and urbanization have put pressure on existing infrastructure, services, and resources.
- Struggle with Infrastructure Development:
The MCD has struggled to keep up with the demand for developing infrastructure like roads, public transportation, and utilities due to inadequate planning and the city’s expansion.
- Persistent Waste Management Issues:
Proper waste management remains a challenge, leading to problems such as improper waste disposal, littering, and environmental pollution.
- Ensuring Sanitation and Public Health:
Providing adequate sanitation and public health services for the growing population is a challenge, with concerns about cleanliness, disease control, and hygiene.
- Dealing with Traffic Congestion and Transportation Problems:
Delhi has faced severe traffic congestion, insufficient public transportation, and air pollution, impacting residents’ quality of life.
- Air Pollution Concerns:
Frequent hazardous air pollution levels in Delhi are primarily caused by vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and crop burning in neighboring states.
- Challenges of Unplanned Urban Development:
The rapid, unplanned growth of the city has led to issues like illegal constructions, encroachments, and violations of zoning regulations.
- Securing Adequate Funding and Resources:
The MCD has encountered difficulties in securing sufficient funding and resources to meet the growing demands for services and infrastructure development.
- Corruption and Governance Challenges:
Like many large municipal bodies, the MCD has faced allegations of corruption, inefficiency, and a lack of transparency in its operations.
- Addressing Economic Disparities:
Ensuring fair distribution of resources and services across all sections of society is a challenge due to Delhi’s diverse population with varying economic backgrounds.
- Providing Quality Education and Healthcare:
Ensuring access to quality education and healthcare services for all residents is a challenge managed by the MCD through schools and health centers.
- Navigating Legal and Regulatory Complexities:
The MCD faces challenges related to navigating legal and regulatory aspects concerning land use, building approvals, and enforcement of regulations.
Initiatives for a Better Delhi
Efforts to improve the quality of life in Delhi have led to various initiatives aimed at addressing the city’s challenges and promoting sustainable development. Here are some notable initiatives that have been undertaken to create a better Delhi:
- Expanded Public Transportation: Efforts to enhance and develop public transportation, such as the Delhi Metro, have eased traffic congestion and lowered pollution. The Metro system has grown with new lines being added.
- Odd-Even Scheme: To combat air pollution, the Delhi government introduced the odd-even scheme, where private vehicle usage is regulated based on license plate numbers, alternating on different days.
- Cleanliness Campaign (Swachh Bharat Abhiyan): A nationwide campaign focuses on enhancing cleanliness and waste management, encouraging proper waste disposal and maintaining clean public spaces.
- Increasing Greenery: Initiatives to boost the city’s green cover involve tree planting drives, afforestation efforts, and the upkeep of parks and green areas.
- Encouraging CNG Usage: The adoption of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for public transport and private vehicles has contributed to reducing air pollution from vehicle emissions.
- E-Rickshaws and Last-Mile Connectivity: Battery-operated e-rickshaws and bicycle-sharing programs have improved convenient and eco-friendly last-mile transportation options.
- Curbing Unauthorized Construction: Steps have been taken to eliminate illegal encroachments and unauthorized constructions, addressing unplanned urban growth and promoting organized development.
- Health and Education Improvement: Focus on better healthcare and education services includes upgrading medical facilities, schools, and creating health awareness initiatives.
- Yamuna River Restoration: Measures have been implemented to rejuvenate the Yamuna River, including sewage interception and treatment to prevent pollution.
- Smart City Initiatives: As part of the Smart Cities Mission, technology-driven solutions are employed to enhance urban infrastructure, services, and overall quality of life.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Promoting rainwater harvesting in residential and commercial areas helps recharge groundwater and tackle water scarcity.
- Preservation of Heritage: Efforts involve restoring and safeguarding historical monuments and sites, promoting cultural heritage and tourism.
- Digital Governance Services: Online platforms for tasks like property tax payment, building permits, and licenses enhance transparency and efficiency in government services.
- Encouraging Electric Mobility: Incentives for electric vehicles and the development of charging infrastructure aim to reduce emissions from conventional vehicles.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Real-time air quality data is gathered from monitoring stations across the city, raising awareness about pollution levels and its impact.
- Sustainable Waste Management: Initiatives for waste segregation, waste-to-energy projects, and recycling work toward improved waste management practices.
- Engaging the Community: Citizens are involved through awareness campaigns, volunteer efforts, and participatory planning to collectively contribute to creating a better city.
Citizen Engagement and Participation
Effective governance and community development depend on citizen engagement and participation. Better outcomes, greater transparency, and more profound sense of community ownership result when citizens actively participate in decision-making processes and shape the rules and procedures that touch their lives. The following are some vital elements of citizen involvement and engagement:
| Strategy | Description |
| Inclusive Decision-Making |
Engaging citizens ensures that a diverse range of perspectives, needs, and concerns are taken into account when making decisions about urban planning, infrastructure development, and public services. This can be done through public consultations, town hall meetings, and other forms of citizen engagement.
|
| Transparency and Accountability |
Open and transparent communication between government authorities and citizens fosters trust and accountability. Citizens have a right to know how decisions are being made and how resources are being allocated. This can be done through regular reporting on government activities, making information about government projects and policies publicly available, and responding to citizen queries and concerns.
|
| Access to Information |
Providing citizens with accurate and timely information about government projects, policies, and budgets empowers them to participate meaningfully in discussions and debates. This can be done through government websites, publications, and other channels.
|
| Public Consultations |
Holding public meetings, forums, and consultations allows citizens to express their opinions, voice concerns, and provide feedback on proposed projects and policies. This can help to ensure that government decisions are made in the best interests of the community.
|
| Collaborative Planning |
Engaging citizens in the planning process helps identify community needs, preferences, and priorities, resulting in more effective and relevant development plans. This can be done through citizen advisory committees, charrettes, and other participatory planning processes.
|
| Community-Based Projects |
Encouraging citizens to initiate and participate in community projects fosters a sense of ownership and pride, leading to improved local infrastructure and services. This can be done through government grants and other support for community-led initiatives.
|
| Participatory Budgeting |
Allowing citizens to directly influence budget allocation decisions ensures that public funds are directed toward projects that align with community needs. This can be done through online platforms, town hall meetings, and other mechanisms.
|
| Digital Platforms |
Utilizing technology and online platforms enables citizens to engage remotely, access information, and participate in discussions and surveys. This can help to increase the reach of citizen engagement efforts and make it easier for citizens to participate.
|
| Capacity Building |
Providing training and education to citizens enhances their ability to understand and engage effectively in governance processes. This can be done through workshops, seminars, and other capacity-building initiatives.
|
| Feedback Mechanisms |
Establishing channels for citizens to provide ongoing feedback about public services, infrastructure, and policies helps identify areas for improvement. This can be done through surveys, suggestion boxes, and other feedback mechanisms.
|
| Collaborative Problem-Solving |
Involving citizens in finding solutions to local challenges leverages their expertise and promotes collective ownership of community issues. This can be done through hackathons, innovation labs, and other collaborative problem-solving initiatives.
|
| Community Empowerment |
Engaged citizens feel a sense of empowerment and are more likely to take an active role in shaping their communities’ development. This can be done through civic education, training, and other initiatives that support citizen empowerment.
|
| Civic Education |
Promoting civic education and awareness campaigns helps citizens understand their rights, responsibilities, and the importance of their participation in governance. This can be done through school programs, public awareness campaigns, and other initiatives.
|
| Youth Engagement |
Involving young people ensures that future generations have a stake in the development of their city and helps cultivate active citizenship from an early age. This can be done through youth councils, youth-led projects, and other initiatives.
|
FAQs
The Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) is a local governing body responsible for managing and administering various aspects of the city of Delhi, India. It plays a crucial role in providing essential services and maintaining infrastructure within its jurisdiction.
The MCD is responsible for a range of tasks, including urban planning, sanitation, waste management, road construction and maintenance, education, healthcare, parks, and local governance services. It aims to improve the quality of life for Delhi’s residents.
The MCD faces challenges like rapid urbanization, population growth, inadequate infrastructure, waste management issues, air pollution, traffic congestion, unplanned urban development, funding constraints, and governance concerns.
The MCD has introduced several initiatives to address these challenges, such as expanding public transportation (like the Delhi Metro), implementing the odd-even scheme for vehicle usage, participating in the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan for cleanliness, promoting green cover expansion, encouraging CNG adoption for vehicles, and more.
The MCD believes in citizen engagement and participation. It conducts public consultations, holds meetings, and encourages community-based projects. It also uses digital platforms for online engagement, participatory budgeting, and feedback collection.



















