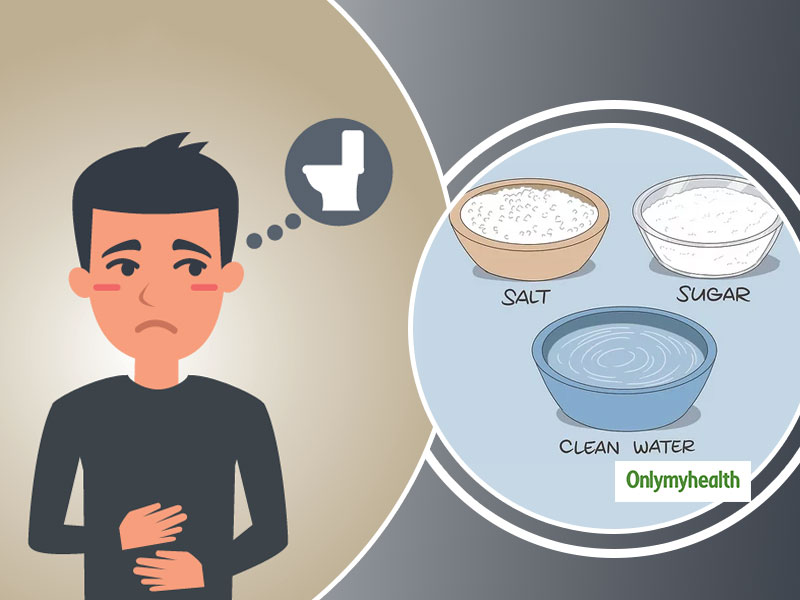
When the body loses more water than it takes in, dehydration develops. Numerous issues, including as weariness, mental disorientation, and even mortality, may result from this. Dehydration is particularly deadly for youngsters.
Oral rehydration solution, or ORS, is a beverage that may be used to both treat and prevent dehydration. Water, sugar, and electrolytes—minerals that the body need for healthy function—make up its composition. ORS aids in replenishing the fluids and electrolytes lost as an outcome of vomiting, diarrhea, or other dehydration-related symptoms.
Dehydration may be treated safely and effectively using ORS. Even young toddlers may easily consume it, and there are no negative side effects. ORS can be manufactured at home or purchased over-the-counter.
Table of Contents
- ORS Full Form: Science Behind ORS
- ORS Full Form: Available Options
- ORS Full Form: When to Choose
- ORS Full Form: For Various Age Groups
- ORS Full Form: Sports & ORS
- ORS Full Form: Myths & Facts
- ORS Full Form: Importance
- ORS Full Form: Related Health Issues
- ORS Full Form: Innovations in ORS Technology
- ORS Full Form: Conlusion
- ORS Full Form: FAQs
The Science Behind Oral Rehydration Solutions

Dehydration spurred on by diarrhea, vomiting, or other causes can be safely and successfully treated with oral rehydration solutions (ORS). They are composed of electrolytes, which are minerals that the human body requires in order to operate correctly, water, sugar, and sugar.
Dehydration may be treated effectively and safely using ORS. Even young children may easily eat it, and there are no negative side effects. ORS can be manufactured at home or bought over-the-counter.
It’s crucial to consult a doctor as quickly as possible if you suspect that you or your kid is dehydrated. Serious dehydration can occur, especially in young infants. However, ORS can assist in preventing dehydration along with consequences with quick treatment.
Commercial ORS: Exploring Available Options
Various commercial ORS products are readily available in the market. Brands like Pedialyte and Ceralyte offer pre-packaged solutions designed to combat dehydration efficiently. These products come in different flavors and are tailored for both children and adults.
here are some commercial ORS options available:
- Pedialyte: Pedialyte is a popular ORS that is available in a variety of flavors, including grape, orange, and strawberry. It is also available in a sugar-free version. Pedialyte is a good option for children and adults who are dehydrated.
- Rehydralyte: Rehydralyte is another popular ORS that is available in a variety of flavors, including lemon-lime, orange, and cherry. It is also available in a sugar-free version. Rehydralyte is a good option for children and adults who are dehydrated.
- Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS): Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) is a generic ORS that is available in powder form. It can be mixed with water to create a solution that is similar to Pedialyte or Rehydralyte.
ORS for Various Age Groups

Here are a few suggestions for administering ORS to persons of various ages:
- Children under 6 months old : You should get medical assistance from your doctor if your infant is younger than 6 months old and is experiencing vomiting or diarrhea. In some circumstances, your doctor might recommend giving your kid ORS.
- Children from 6 months to 5 years old : If a child between the ages of 6 months and 5 suffers diarrhea or vomiting, ORS should be administered. Every time your child passes a watery stool, you can give them ORS. If your child keeps throwing up, you can also provide ORS to them. You might need to provide lower doses of ORS more often if your kid is throwing up.
- Children over 5 years old and adults: Adults with diarrhea or vomiting and children older than 5 years old should get ORS. Every time your kid or adult passes a watery stool, you can give them ORS. If your kid or adult is throwing up, you can also give them ORS. You might need to give your kid or adult lower doses of ORS frequently if they are throwing up.
Sports and ORS: A Winning Hydration Strategy
| Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Fluid intake | Aim to drink 16-24 ounces of fluid 2-3 hours before exercise. During exercise, drink 6-12 ounces of fluid every 15-20 minutes. After exercise, drink 24-32 ounces of fluid for every pound of weight lost. |
| Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) | ORS can be a good option for athletes who are losing fluids and electrolytes at a high rate. ORS typically contain glucose, sodium, and potassium, which can help to replace fluids and electrolytes lost through sweat. |
| Signs of dehydration | Signs of dehydration include thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, headache, dizziness, and muscle cramps. If you experience any of these signs, it is important to drink fluids immediately. |
| Special considerations | Athletes who participate in high-intensity or endurance sports, or who compete in hot weather, are at increased risk of dehydration. These athletes should be especially vigilant about staying hydrated. |
ORS Myths and Facts
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| ORS is only for children. | ORS can be used by people of all ages, including adults and infants. |
| You can make your own ORS at home. | It is possible to make your own ORS at home, but it is important to use the correct proportions of ingredients. The World Health Organization (WHO) has a standard recipe for ORS that can be found on their website. |
| ORS is too sweet. | ORS does contain sugar, but it is not as sweet as soda or other sugary drinks. The sugar in ORS helps to absorb the fluids and electrolytes in the solution. |
| ORS is not effective for adults. | ORS is effective for people of all ages, including adults. In fact, a study published in the journal “The Lancet” found that ORS was just as effective as intravenous fluids for treating dehydration in adults with diarrhea. |
| ORS can cause diarrhea. | ORS does not cause diarrhea. In fact, ORS can actually help to prevent diarrhea by replacing the fluids and electrolytes lost through diarrhea. |
Staying Prepared: Importance of Keeping ORS Handy
Combating Dehydration-Related Health Issues
When the body loses more fluids than it takes in, dehydration develops. This may result in a number of health issues, such as:
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Muscle cramps
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Kidney failure
- Death
The Future of Hydration: Innovations in ORS Technology
The study and creation of fresh and enhanced ORS formulations has garnered growing attention in recent years. The following are some of the main ORS technological innovation areas:
- New ingredients: A new generation of ORS components, including amino acids, probiotics, and prebiotics, are being studied by researchers. These components can improve the absorption of fluids and electrolytes and aid in the prevention of diarrhea and other dehydration-related issues.
- New delivery methods: ORS is frequently sold as a powder that must be dissolved with water. However, scientists are working on fresh ORS delivery systems, such sachets, pills, and even patches. In distant places or during emergencies, these methods of administration may make it simpler for patients to take ORS.
- Personalized ORS: Right now, ORS is a universally applicable solution. However, scientists are creating individualized ORS formulations that are catered to the requirements of each patient. For instance, customized ORS might be modified based on the individual’s age, weight, and health.
Conclusion
FAQs
Most Popular Links
Career Tests

Graduates & Post Graduates

21st Century Skills & Learning Test Grade 12

21st Century Skills & Learning Test Grade 11

21st Century Skills & Learning Test Grade 10

PSYCHOMETRIC IDEAL CAREER TEST™

PSYCHOMETRIC SKILL BASED TEST FOR 9TH

PSYCHOMETRIC ENGINEERING SELECTOR

PSYCHOMETRIC EDUCATOR PROFESSIONAL SKILLS

PSYCHOMETRIC STREAM SELECTOR™

PSYCHOMETRIC COMMERCE CAREER SELECTOR

PSYCHOMETRIC HUMANITIES CAREER SELECTOR

PSYCHOMETRIC PROFESSIONAL SKILL INDEX
When the body loses more water than it takes in, dehydration develops. Numerous issues, including as weariness, mental disorientation, and even mortality, may result from this. Dehydration is particularly deadly for youngsters.
Oral rehydration solution, or ORS, is a beverage that may be used to both treat and prevent dehydration. Water, sugar, and electrolytes—minerals that the body need for healthy function—make up its composition. ORS aids in replenishing the fluids and electrolytes lost as an outcome of vomiting, diarrhea, or other dehydration-related symptoms.
Dehydration may be treated safely and effectively using ORS. Even young toddlers may easily consume it, and there are no negative side effects. ORS can be manufactured at home or purchased over-the-counter.
Table of Contents
- ORS Full Form: Science Behind ORS
- ORS Full Form: Available Options
- ORS Full Form: When to Choose
- ORS Full Form: For Various Age Groups
- ORS Full Form: Sports & ORS
- ORS Full Form: Myths & Facts
- ORS Full Form: Importance
- ORS Full Form: Related Health Issues
- ORS Full Form: Innovations in ORS Technology
- ORS Full Form: Conlusion
- ORS Full Form: FAQs
The Science Behind Oral Rehydration Solutions

Dehydration spurred on by diarrhea, vomiting, or other causes can be safely and successfully treated with oral rehydration solutions (ORS). They are composed of electrolytes, which are minerals that the human body requires in order to operate correctly, water, sugar, and sugar.
Dehydration may be treated effectively and safely using ORS. Even young children may easily eat it, and there are no negative side effects. ORS can be manufactured at home or bought over-the-counter.
It’s crucial to consult a doctor as quickly as possible if you suspect that you or your kid is dehydrated. Serious dehydration can occur, especially in young infants. However, ORS can assist in preventing dehydration along with consequences with quick treatment.
Commercial ORS: Exploring Available Options
Various commercial ORS products are readily available in the market. Brands like Pedialyte and Ceralyte offer pre-packaged solutions designed to combat dehydration efficiently. These products come in different flavors and are tailored for both children and adults.
here are some commercial ORS options available:

- Pedialyte: Pedialyte is a popular ORS that is available in a variety of flavors, including grape, orange, and strawberry. It is also available in a sugar-free version. Pedialyte is a good option for children and adults who are dehydrated.
- Rehydralyte: Rehydralyte is another popular ORS that is available in a variety of flavors, including lemon-lime, orange, and cherry. It is also available in a sugar-free version. Rehydralyte is a good option for children and adults who are dehydrated.
- Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS): Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) is a generic ORS that is available in powder form. It can be mixed with water to create a solution that is similar to Pedialyte or Rehydralyte.
ORS for Various Age Groups

Here are a few suggestions for administering ORS to persons of various ages:
- Children under 6 months old : You should get medical assistance from your doctor if your infant is younger than 6 months old and is experiencing vomiting or diarrhea. In some circumstances, your doctor might recommend giving your kid ORS.
- Children from 6 months to 5 years old : If a child between the ages of 6 months and 5 suffers diarrhea or vomiting, ORS should be administered. Every time your child passes a watery stool, you can give them ORS. If your child keeps throwing up, you can also provide ORS to them. You might need to provide lower doses of ORS more often if your kid is throwing up.
- Children over 5 years old and adults: Adults with diarrhea or vomiting and children older than 5 years old should get ORS. Every time your kid or adult passes a watery stool, you can give them ORS. If your kid or adult is throwing up, you can also give them ORS. You might need to give your kid or adult lower doses of ORS frequently if they are throwing up.
Sports and ORS: A Winning Hydration Strategy
| Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Fluid intake | Aim to drink 16-24 ounces of fluid 2-3 hours before exercise. During exercise, drink 6-12 ounces of fluid every 15-20 minutes. After exercise, drink 24-32 ounces of fluid for every pound of weight lost. |
| Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) | ORS can be a good option for athletes who are losing fluids and electrolytes at a high rate. ORS typically contain glucose, sodium, and potassium, which can help to replace fluids and electrolytes lost through sweat. |
| Signs of dehydration | Signs of dehydration include thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, headache, dizziness, and muscle cramps. If you experience any of these signs, it is important to drink fluids immediately. |
| Special considerations | Athletes who participate in high-intensity or endurance sports, or who compete in hot weather, are at increased risk of dehydration. These athletes should be especially vigilant about staying hydrated. |
ORS Myths and Facts
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| ORS is only for children. | ORS can be used by people of all ages, including adults and infants. |
| You can make your own ORS at home. | It is possible to make your own ORS at home, but it is important to use the correct proportions of ingredients. The World Health Organization (WHO) has a standard recipe for ORS that can be found on their website. |
| ORS is too sweet. | ORS does contain sugar, but it is not as sweet as soda or other sugary drinks. The sugar in ORS helps to absorb the fluids and electrolytes in the solution. |
| ORS is not effective for adults. | ORS is effective for people of all ages, including adults. In fact, a study published in the journal “The Lancet” found that ORS was just as effective as intravenous fluids for treating dehydration in adults with diarrhea. |
| ORS can cause diarrhea. | ORS does not cause diarrhea. In fact, ORS can actually help to prevent diarrhea by replacing the fluids and electrolytes lost through diarrhea. |
Staying Prepared: Importance of Keeping ORS Handy
Combating Dehydration-Related Health Issues
When the body loses more fluids than it takes in, dehydration develops. This may result in a number of health issues, such as:
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Muscle cramps
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Kidney failure
- Death
The Future of Hydration: Innovations in ORS Technology
The study and creation of fresh and enhanced ORS formulations has garnered growing attention in recent years. The following are some of the main ORS technological innovation areas:
- New ingredients: A new generation of ORS components, including amino acids, probiotics, and prebiotics, are being studied by researchers. These components can improve the absorption of fluids and electrolytes and aid in the prevention of diarrhea and other dehydration-related issues.
- New delivery methods: ORS is frequently sold as a powder that must be dissolved with water. However, scientists are working on fresh ORS delivery systems, such sachets, pills, and even patches. In distant places or during emergencies, these methods of administration may make it simpler for patients to take ORS.
- Personalized ORS: Right now, ORS is a universally applicable solution. However, scientists are creating individualized ORS formulations that are catered to the requirements of each patient. For instance, customized ORS might be modified based on the individual’s age, weight, and health.
Conclusion
FAQs
Most Popular Links
Career Tests

Graduates & Post Graduates

21st Century Skills & Learning Test Grade 12

21st Century Skills & Learning Test Grade 11

21st Century Skills & Learning Test Grade 10

PSYCHOMETRIC IDEAL CAREER TEST™

PSYCHOMETRIC SKILL BASED TEST FOR 9TH

PSYCHOMETRIC ENGINEERING SELECTOR

PSYCHOMETRIC EDUCATOR PROFESSIONAL SKILLS

PSYCHOMETRIC STREAM SELECTOR™

PSYCHOMETRIC COMMERCE CAREER SELECTOR

PSYCHOMETRIC HUMANITIES CAREER SELECTOR

PSYCHOMETRIC PROFESSIONAL SKILL INDEX
Category
Popular Full Forms
Most Viewed Full Forms
Popular Full Forms
Top Private Universities
Most Popular Universities
Trending Colleges
Career Counselling Services
Popular Exams
Most Popular Article's
SCHOOLS
- Counselling Services For School
- Counselling Services For 9th Class
- Counselling Services For 10th Class
- Counselling Services For 11th Class
- Counselling Services For 12th Class
- Competitive Exam Calendars
- Engineering Entrance Exam
- Medical Entrance Exam
- Management Entrance Exam
- MBA Entrance Exams
- XAT
- MAT
- NMAT
- IIAD
STUDENTS
- For 9th class
- Skill Based Career Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For 10th class
- Stream Selector Test |
- Ideal Career Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For 11th class
- Ideal Career Test |
- Engineering Branch Selector |
- Humanities Career Selector |
- Commerce Career Selector |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan|
- Mentorship Plan
- For 12th class
- Ideal Career Test |
- Engineering Branch Selector |
- Humanities Career Selector |
- Commerce Career Selector |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For B.Com
- Commerce Career Selector |
- Ideal Career Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For B.Sc
- Ideal Career Test |
- Professional Skill Index Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For B.Tech
- Ideal Career Test |
- Professional Skill Index Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For B.A
- Ideal Career Test |
- Humanities Career Selector |
- Professional Skill Index Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For MBA
- Ideal Career Test |
- Professional Skill Index Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
- For Masters
- Professional Skill Index Test |
- Services |
- Basic Plan |
- Advance Plan |
- Video Counselling Plan |
- Mentorship Plan
STUDY ABROAD







