The Line of Actual Control (LAC) is the de facto border between India and China. It is a notional line that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory. The LAC is not an internationally recognized border, and there are still some areas of dispute between the two countries.
Introduction to LAC
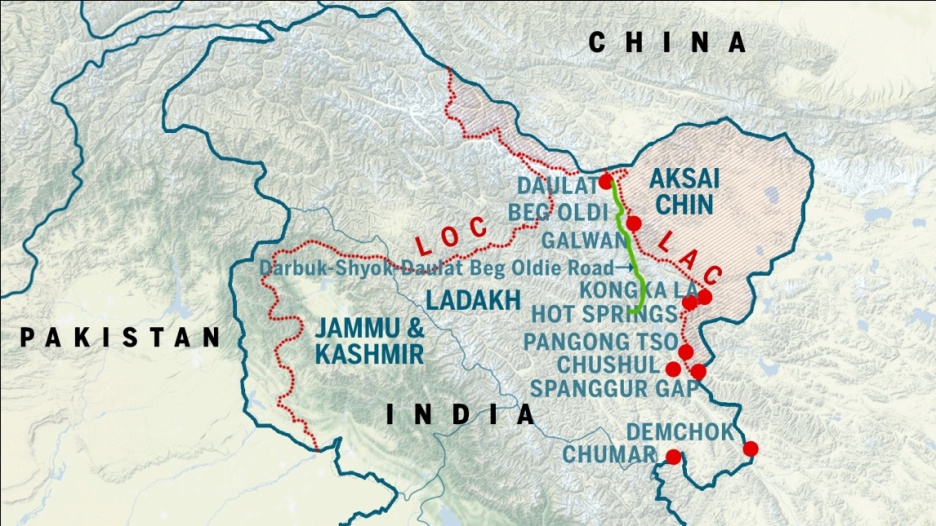
In the realm of geopolitical boundaries, where nations’ territories converge, tensions can simmer, and histories interweave, the Line of Actual Control (LAC) stands as an enigmatic demarcation that captures attention and sparks discussions. Spanning the rugged terrain between two of Asia’s most populous and influential nations, India and China, the LAC encapsulates complex histories, strategic interests, and occasional flare-ups that underscore the complexities of modern international relations. This blog embarks on a journey to demystify the Line of Actual Control, unravel its origins, shed light on its implications, and examine the challenges that have both tested and shaped the diplomatic landscape between these two nations.
Historical Context: Origins of the LAC
To comprehend the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and its significance, one must delve into the historical context that shaped its emergence. Rooted in a complex history of territorial disputes and geopolitical rivalries, the LAC serves as a reminder of the challenges that have long defined the relationship between India and China.
Sino-Indian Border Conflict: 1962 The roots of the LAC can be traced back to the 1962 Sino-Indian border conflict, a significant turning point in the relationship between the two nations. This conflict, often referred to as the Sino-Indian War, erupted over territorial disputes in the Himalayan region. As tensions escalated, the military confrontation resulted in a ceasefire and a standstill in 1962. It was during these turbulent times that the concept of the LAC began to take shape.
Establishing a Temporary Boundary In the aftermath of the conflict, both India and China recognized the need for a temporary boundary that would prevent further military clashes. The LAC was thus conceived as a line that neither side would militarily cross, serving as a de facto boundary while diplomatic negotiations continued. However, the LAC’s definition remained vague, leading to differing perceptions of its location and contributing to ongoing tensions.
Challenges of Ambiguity
Loosely Demarcated Boundaries: The foremost challenge of the LAC is its lack of clear and universally agreed-upon demarcation. This lack of specificity stems from historical reasons, making it susceptible to differing interpretations by both India and China. The absence of precise coordinates can lead to misunderstandings and unintended transgressions.
Disputed Territories and Overlapping Claims: The ambiguity surrounding the LAC fuels territorial disputes. Both nations lay claim to specific regions, resulting in overlapping assertions of sovereignty. This complicates matters as patrols and military presence come in close proximity, raising the risk of incidents that can escalate tensions.
Navigating Differing Perceptions: The differing perceptions of the LAC’s location add complexity to the issue. India and China often have conflicting views on where the line lies, making it challenging to maintain a shared understanding. These differences can lead to incidents where one nation perceives the other as violating the LAC.
Border Incursions and Tensions
The Line of Actual Control (LAC) that separates India and China is more than a mere geographic reference; it’s a line that often teeters on the edge of tension and confrontation. The ambiguous nature of the LAC, coupled with differing perceptions of its location, has led to periodic border incursions and standoffs between the two nations. In this section, we delve into the incidents that have ignited tensions and tested the diplomatic resilience of India and China.
The Galwan Valley Clash (2020): One of the most significant and tragic incidents in recent times was the clash between Indian and Chinese troops in the Galwan Valley. The confrontation resulted in casualties on both sides and sent shockwaves through international relations. The incident underscored the potential volatility of the LAC and the need for effective communication mechanisms to prevent escalation.
Doklam Standoff (2017): While not directly on the LAC, the Doklam standoff exemplifies the intricacies of the border disputes. Located near the tri-junction of India, China, and Bhutan, the area witnessed a tense standoff between Indian and Chinese troops over road construction. The incident highlighted the vulnerability of areas adjacent to the LAC and the complex geopolitical dynamics at play.
Intrusions and Patrols: Border incursions along the LAC are not uncommon. Both India and China conduct patrols near disputed areas, often leading to face-offs as troops encounter each other. These incidents highlight the delicate balance between asserting sovereignty and avoiding escalation.
Strategic Significance of LAC
Beyond its role as a demarcation between two nations, the Line of Actual Control (LAC) holds a strategic significance that extends into the realms of security, resources, and regional influence. The areas along the LAC are not merely pieces of land; they are key chess pieces in a complex geopolitical game. In this section, we delve into the strategic importance of the LAC and the implications it carries for India, China, and the broader region.
Access to Resources: Certain regions along the LAC are rich in natural resources, ranging from minerals to water sources. Control over these resources can bolster a nation’s economic and industrial capabilities, leading to a vested interest in asserting sovereignty over these areas.
Strategic Military Advantage: The high-altitude terrain and mountainous landscapes along the LAC provide strategic advantages for military positioning. Controlling vantage points can offer a significant edge in monitoring activities on the other side, as well as projecting influence over neighboring regions.
Security Concerns: The proximity of military forces along the LAC raises concerns about national security. The potential for clashes, misunderstandings, and border incursions necessitates constant vigilance and readiness, particularly in areas where military presence is concentrated.
Diplomatic Efforts and Agreements
Amidst the complex challenges posed by the Line of Actual Control (LAC), both India and China have recognized the imperative of diplomacy as a means to prevent misunderstandings, defuse tensions, and ensure stability along their shared border. This section delves into the diplomatic efforts and agreements that have been pivotal in managing the complexities of the LAC.
Bilateral Talks and Negotiations: India and China have engaged in a series of bilateral talks and negotiations to address border disputes and maintain peace along the LAC. These discussions, often conducted at various levels of the diplomatic and military hierarchy, aim to find common ground, establish communication channels, and manage potential conflicts.
Five-Point Consensus: In 2020, amid heightened tensions following the Galwan Valley clash, India and China issued a joint statement outlining a “five-point consensus” to guide their relations. This consensus emphasized measures to disengage and de-escalate, including respecting existing agreements, avoiding actions that could escalate tensions, and working together to maintain peace and tranquility along the LAC.
Key Agreements and Their Impact
1993 Agreement on Peace and Tranquility: Signed between India and China in 1993, this agreement established the foundation for maintaining peace along the LAC. It emphasizes the need to exercise restraint, avoid the use of force, and prevent military activities that could escalate tensions. The agreement’s principles have been instrumental in preventing large-scale conflicts along the border.
Confidence-Building Measures (CBMs): Part of the 1993 agreement, CBMs aim to build trust and transparency between India and China. These measures include notifying each other about military exercises, prohibiting live-fire drills within a certain distance of the LAC, and conducting joint military exercises to enhance understanding.
Impact and Challenges: These agreements have contributed significantly to maintaining stability and preventing large-scale conflicts along the LAC. They have created mechanisms for communication, crisis management, and confidence-building. However, challenges persist due to differing perceptions of the LAC’s location and historical sensitivities, which can lead to incidents and standoffs.
Regional Implications
Neighboring Nations: The LAC’s proximity to other nations, particularly Bhutan and Nepal, influences their security and foreign policy choices. Bhutan, in particular, shares a border with China and has its own disputes, emphasizing the interconnectedness of regional dynamics.
Security Complexities: The instability along the LAC has led neighboring nations to closely monitor developments. Concerns about border incidents, standoffs, and the potential for escalation can influence defense strategies and alignments in the region.
Influence of Global Powers: Global powers like the United States and Russia keep a watchful eye on the LAC’s developments due to the broader implications for regional stability and their own strategic interests. Their engagement can either exacerbate tensions or facilitate diplomatic efforts.
Conclusion
The Line of Actual Control remains a complex and fluid boundary, emblematic of historical rivalries, geopolitical sensitivities, and strategic maneuvering. Its challenges reflect the complexities of border disputes in a rapidly changing world. As India and China navigate their relationships and work towards mutual understanding, the management of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) remains an ongoing test of diplomacy and cooperation, with far-reaching consequences for regional stability and international relations.
FAQs
The Line of Actual Control is a loosely defined boundary that separates the territories controlled by India and China. It emerged after the 1962 Sino-Indian border conflict as a temporary demarcation to prevent further military clashes.
The LAC lacks precise coordinates and clear demarcation, leading to differing perceptions of its location by India and China. This ambiguity contributes to border disputes and tensions.
Notable incidents include the Galwan Valley clash in 2020, the Doklam standoff in 2017, and periodic border incursions. These incidents have tested diplomatic relations and highlighted the potential for escalation.
Both nations engage in bilateral talks, negotiations, and agreements aimed at maintaining peace and stability. Mechanisms like the Working Mechanism for Consultation and Coordination (WMCC) and Border Personnel Meetings (BPMs) facilitate communication and crisis management.



















