A Document Management System (DMS) is a sophisticated software solution designed to efficiently handle the creation, storage, retrieval, management, and tracking of electronic documents and files within an organization. It serves as a comprehensive digital repository for all types of documents, from text files and spreadsheets to images and multimedia files.
Types of DMS
Document Management Systems (DMS) come in various types, tailored to specific organizational needs:
- On-Premises DMS: Traditional, self-hosted with full control.
- Cloud-Based DMS: Hosted remotely for scalability and accessibility.
- Open Source DMS: Customizable, with source code access.
- ECM Systems: Comprehensive, for large enterprises.
- Document Imaging DMS: Specialized in paper document digitization.
- Legal DMS: Compliance-focused, for law firms.
- Records Management: Ensures regulatory compliance.
- Collaboration DMS: Prioritizes teamwork and workflows.
- Workflow Management: Streamlines automated workflows.
- Document Archiving: Focuses on long-term storage.
- Mobile DMS: Optimized for mobile access and collaboration.
- Industry-Specific DMS: Tailored for specific sectors.
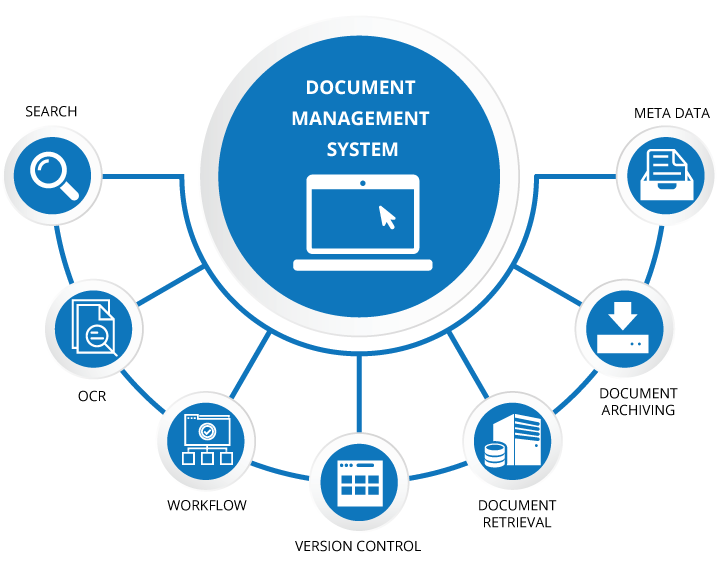
Key Components of a DMS
A Document Management System (DMS) comprises essential components:
- Document Capture: Input documents from various sources.
- Storage Repository: Central storage with organization and indexing.
- Document Retrieval: Robust search and retrieval functions.
- Version Control: Tracking and managing document versions.
- Access Control and Security: Ensures data protection and compliance.
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitates simultaneous document work.
- Workflow Automation: Streamlines document-based processes.
- Integration Capabilities: Links with other business systems.
- Compliance and Records Management: Supports regulatory adherence.
- Document Lifecycle Management: Tracks document lifecycles.
- Document Archiving: Moves less-used documents to long-term storage.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides insights for improvement.
Document Scanning and Digitization
Document scanning and digitization convert physical documents into electronic formats, offering numerous benefits:
- Scanning: Specialized equipment captures paper documents digitally, specifying resolution and format.
- Image Capture: Pages are scanned and saved as PDF, JPEG, or TIFF files.
- OCR: Optical Character Recognition recognizes text in images, making it searchable and editable.
- Metadata and Indexing: Documents are tagged with metadata and indexed for quick retrieval.
- Quality Control: Processes ensure accurate representation of paper documents.
- Storage: Digital documents are stored in a central repository, like a Document Management System (DMS) or cloud storage.
- Access: Documents can be accessed remotely, facilitating remote work and collaboration.
- Backup: Digital documents are less vulnerable to physical damage and are regularly backed up.
- Cost Savings: Digitization reduces storage and printing costs while streamlining document management.
DMS Trends and Future Developments
Document Management Systems (DMS) have evolved with these trends:
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud DMS for scalability and accessibility
AI Advancements: AI for document processing, search, and automation.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain for document security and authenticity
- Mobile Access: Mobile apps for on-the-go document management.
- Enhanced Security: Stronger encryption and compliance measures.
- Productivity Tool Integration: Seamless integration with popular tools.
- Voice and NLP: Voice commands and natural language interaction.
- AI Data Tagging: AI-driven classification and tagging.
- Advanced Analytics: Insights for document usage and compliance.
- Hybrid Solutions: Combining on-premises and cloud-based systems.
- Sustainability: Focus on reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Document Management Systems (DMS) have emerged as indispensable tools in the modern digital landscape. They have evolved to meet the growing demands of organizations seeking efficient, secure, and compliant ways to handle documents and data. DMS solutions offer a wide range of capabilities, including document capture, storage, retrieval, and collaboration, all while prioritizing security and compliance.
As we look ahead, DMS trends indicate a continued reliance on cloud-based solutions, integration with advanced technologies like AI and blockchain, and a focus on mobility and sustainability.
FAQs About DMS
Organizations use DMS to streamline document-related processes, improve efficiency, enhance data security, ensure compliance with regulations, reduce paper usage, and facilitate collaboration among teams.
A DMS can manage various types of documents, including text documents, images, spreadsheets, PDFs, emails, and multimedia files.
DMS enhances security through features like access controls, encryption, user authentication, and audit trails, ensuring that sensitive documents are protected from unauthorized access or breaches.
Yes, DMS solutions come in various sizes and can be tailored to the needs of small businesses. Cloud-based DMS, in particular, offers scalability and cost-effectiveness for small organizations.



















