An Information System (IS) is a system composed of hardware, software, data, people, and procedures designed to collect, store, process, and distribute information for various purposes within an organization or to support decision-making. Information systems are fundamental tools used in businesses, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and virtually all sectors of modern society.
Introduction to IS
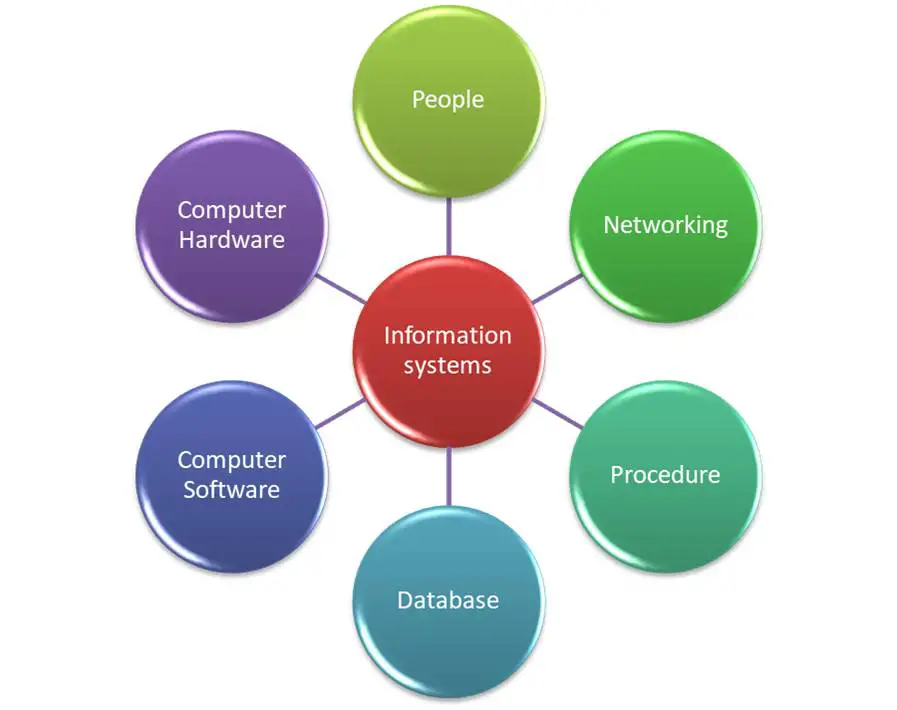
Information systems (IS) are at the heart of modern organizations, playing a crucial role in managing and leveraging information for decision-making, operations, and strategic planning. These systems have become indispensable tools in today’s digital age. This introduction provides an overview of information systems, their significance, and their evolution.
Key Points:
- Definition and Concept: Information systems refer to the combination of hardware, software, data, people, and procedures that work together to collect, process, store, and disseminate information for various purposes within an organization.
- Importance in Modern Organizations: Information systems are vital for organizations to function efficiently and competitively in a data-driven world. They support decision-making, streamline operations, enhance communication, and facilitate innovation.
Components of an Information System
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardware | Physical equipment used for data processing and storage. Includes CPU, storage devices, input/output devices, and networking equipment. |
| Software | Programs and applications that instruct hardware on how to process and manipulate data. Includes operating systems, application software, DBMS, middleware, and firmware. |
| Data | Raw facts and figures in various forms, such as text, numbers, images, or multimedia. |
| People | Individuals involved in the IS, including end users, system administrators, developers, and support staff. |
| Procedures | Protocols, guidelines, and rules for using and managing the information system. |
| Networks | Infrastructure that enables data exchange and connectivity within and outside the organization. Includes wired and wireless networks, internet connectivity, and data transmission protocols. |
Types of Information Systems
| Type of Information System | Description |
|---|---|
| Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) | Systems that process routine transactions and record data in real-time. Commonly used in accounting, inventory management, and order processing. |
| Management Information Systems (MIS) | Systems that provide summarized, structured information to support managerial decision-making and reporting. |
| Decision Support Systems (DSS) | Systems designed to assist in complex, non-routine decisions by providing interactive tools and data analysis capabilities. |
| Executive Information Systems (EIS) | Information systems tailored for top-level executives, providing strategic information for high-level decision-making. |
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems | Integrated systems that manage core business processes, including finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain, to improve efficiency and coordination. |
| Business Intelligence (BI) Systems | Systems that collect, analyze, and present data to help organizations make informed decisions and gain insights. |
Information System Development
- System Development Life Cycle (SDLC): SDLC is a structured framework that guides the development process of an information system. It typically includes phases like planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
- Agile Development: Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, emphasize flexibility and collaboration in system development. They allow for iterative development, frequent feedback, and adaptive changes to better align with evolving business needs.
- User Requirements: Understanding user requirements is a critical initial step in development. It involves gathering and documenting user needs, expectations, and system functionalities.
- System Design: In the design phase, system architects create detailed specifications for the hardware, software, and user interface components of the system. It includes data modeling, architectural planning, and user interface design.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Storage | DBMS stores data in structured formats, such as tables, rows, and columns, facilitating organization and retrieval. |
| Data Retrieval | Users can query the database using structured query languages (e.g., SQL) to retrieve specific data from the database. |
| Data Security | DBMS includes security features to control data access, modifications, and deletions, ensuring data privacy and protection. It implements user authentication and authorization mechanisms. |
| Data Integrity | DBMS enforces data integrity by applying constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, and data validation rules, maintaining data accuracy and consistency. |
| Concurrency Control | In multi-user environments, DBMS manages concurrent data access to prevent conflicts and ensure data consistency during simultaneous transactions. |
| Backup and Recovery | DBMS provides tools and mechanisms for data backup and recovery, safeguarding against data loss due to hardware failures or disasters. |
Networking and Communication
- Local Area Networks (LANs): LANs are networks that cover a limited geographic area, typically within a single building or campus. They provide high-speed data connectivity for devices like computers, printers, and servers.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs cover larger geographic areas, connecting LANs and remote locations over long distances. The internet itself is a global WAN. WANs use various technologies, including leased lines and internet connections.
- Internet and Intranet: The internet is a global network of interconnected devices and networks, providing access to a vast amount of information and services. Intranets are private networks within organizations that use internet technologies to share information and resources internally.
Information Security
- Confidentiality: Information security aims to maintain the confidentiality of sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized users can access it. Encryption, access controls, and user authentication are common measures.
- Integrity: Information must remain intact and unaltered during storage, transmission, and processing. Techniques such as checksums and digital signatures help verify data integrity.
- Availability: Information should be available and accessible when needed. Redundancy, backup systems, and disaster recovery plans ensure data availability even in the face of hardware failures or cyberattacks.
- Authentication: Verification of user identity through usernames, passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial for controlling access to systems and data.
- Authorization: Authorization mechanisms determine what actions users or entities are allowed to perform once authenticated. Role-based access control (RBAC) and permissions are common methods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, information systems are integral to modern organizations, facilitating data management, decision-making, and communication. They encompass a wide range of components, from hardware and software to data, people, and procedures. These systems come in various types, each tailored to specific organizational needs.
Effective development and management of information systems involve structured processes like the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and agile methodologies. These processes ensure that systems meet user requirements, maintain data security, and adhere to quality standards.
FAQs
An information system (IS) is a combination of hardware, software, data, people, and procedures designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information for various purposes within an organization.
The key components of an information system include hardware, software, data, people, and procedures. Networks and communication infrastructure also play a crucial role.
A DBMS manages and organizes data in databases, making it easier to store, retrieve, and manipulate data efficiently. It ensures data integrity, security, and structured storage.
Information security, or cybersecurity, safeguards data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access, breaches, and other cyber threats. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.



















