The Critical Care Unit (CCU) stands as a specialized and essential component within a healthcare facility, dedicated to delivering intensive medical care to patients in critical conditions. Situated at the heart of emergency medical response, the CCU is designed to provide immediate and comprehensive treatment to individuals facing life-threatening illnesses or injuries.
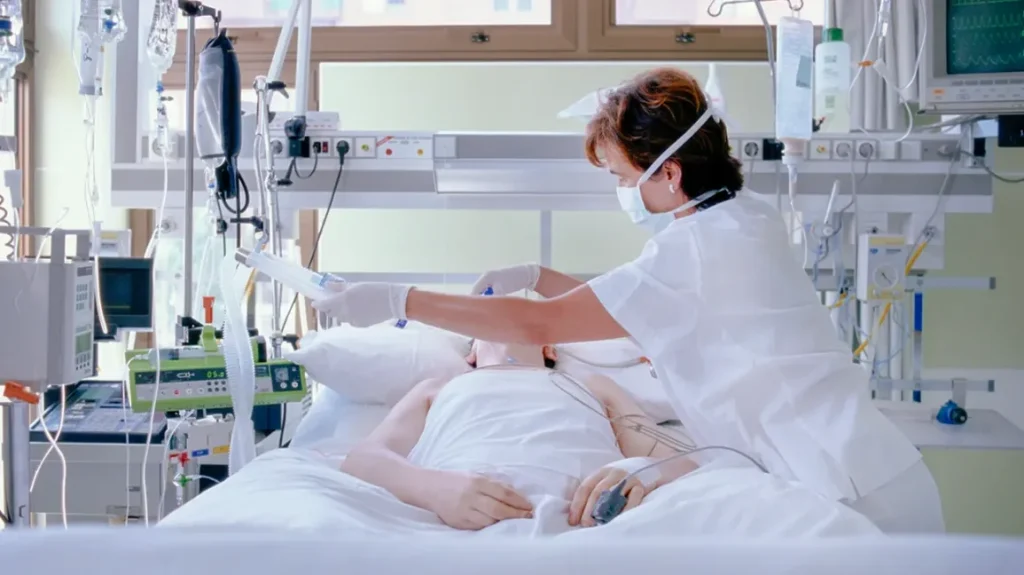
Importance of the CCU
The Critical Care Unit (CCU) is of immense importance in the healthcare sector due to its important role in the management of critically ill patients, it can provide advanced medical services and specialized equipment necessary to stabilize and ensure patient condition to be saved.
In the CCU, medical professionals with specialized training are equipped to handle critical cases, closely monitor vital signs, administer specialized medications, and perform intricate procedures. This level of care is especially vital for patients who require constant supervision, such as those with severe cardiac conditions, respiratory distress, or post-surgery complications.
Differences Between CCU and ICU
| Aspect | CCU (Critical Care Unit) | ICU (Intensive Care Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Primarily cardiac conditions | Various critical illnesses |
| Specialization | Cardiac care | Multi-specialty care |
| Patient Population | Acute cardiac cases | Wide range of critical cases |
Medical Staff in the CCU
In the CCU, medical professionals with specialized training are equipped to handle critical cases, closely monitor vital signs, administer specialized medications, and perform intricate procedures. This level of care is especially vital for patients who require constant supervision, such as those with severe cardiac conditions, respiratory distress, or post-surgery complications.
- Intensivists: Intensivists are specialized doctors who are trained in critical care medicine. They play a central role in overseeing patient care, making crucial medical decisions, and coordinating the overall treatment plan.
- Critical Care Nurses: Critical care nurses are the backbone of the CCU team. They provide direct patient care, closely monitor vital signs, administer medications, and ensure patients are comfortable and stable. Their expertise in managing complex medical situations is invaluable.
- Respiratory Therapists: Respiratory therapists are responsible for managing patients’ respiratory needs, including administering oxygen therapy, ventilator management, and respiratory assessments.
- Pharmacists: Pharmacists collaborate with the team to ensure proper medication administration, dosages, and interactions. They play a critical role in tailoring medications to each patient’s condition.
- Medical Technologists: Medical technologists perform various diagnostic tests and laboratory work that aids in patient assessment and treatment decisions.
Conditions Treated in the CCU
The Critical Care Unit (CCU) specializes in treating a wide range of critical medical conditions that require intensive monitoring, specialized interventions, and immediate medical attention. Some of the conditions treated in the CCU include:
1. Cardiac Emergencies:
- Acute Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
- Severe Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeat)
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- Cardiogenic Shock
2. Respiratory Distress:
- Acute Respiratory Failure
- Severe Pneumonia
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
3. Neurological Emergencies:
- Stroke (Ischemic or Hemorrhagic)
- Traumatic Brain Injury
- Seizures
4. Trauma and Surgical Complications:
- Multiple Trauma
- Post-Surgical Complications
- Severe Burns
5. Sepsis and Septic Shock:
- Systemic Infections Leading to Organ Dysfunction
- Septic Shock with Low Blood Pressure
Equipment and Technology
In the Critical Care Unit (CCU), a comprehensive array of advanced medical equipment and cutting-edge technology is deployed to provide essential care to critically ill patients. This assortment of tools plays a pivotal role in facilitating precise monitoring, accurate diagnostics, and effective treatment interventions.
- Cardiac Monitoring Equipment: CCUs are outfitted with electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) machines that continuously track patients’ heart rhythms, enabling prompt detection of irregularities. Hemodynamic monitors assess vital parameters such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, offering real-time insights into cardiac performance.
- Respiratory Support Devices: Ventilators are instrumental in delivering mechanical ventilation to patients with compromised respiratory function. These devices meticulously control airflow, oxygen levels, and airway pressure to ensure optimal lung function. Pulse oximeters provide noninvasive monitoring of blood oxygen saturation levels.
- Intravenous Therapy Tools: Infusion pumps regulate the administration of medications, fluids, and nutrients through intravenous lines, ensuring precise dosages and rates for maintaining stability.
Conclusion
In the realm of healthcare, the Critical Care Unit (CCU) emerges as a sanctuary where lives hang in the balance, tended to by dedicated medical professionals. This sacred space is where expertise meets empathy, and innovation intertwines with compassion. Through this journey, we’ve witnessed the pivotal role CCUs play in the lives of patients facing critical medical conditions. The CCU stands as a beacon of hope, where advanced technology converges with skilled hands to orchestrate healing journeys.
FAQ'S about CCU
The CCU is specifically designed to care for patients with life-threatening conditions. It offers more advanced monitoring, specialized equipment, and a higher nurse-to-patient ratio compared to other units.
CCUs typically treat patients with conditions such as severe cardiac issues, respiratory failure, post-surgery complications, organ failure, and other critical medical conditions.
The CCU is staffed with a multidisciplinary team including doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other specialists trained in critical care medicine.
Patient care in the CCU involves continuous monitoring, specialized interventions, medications, and treatments tailored to each patient’s condition.



















